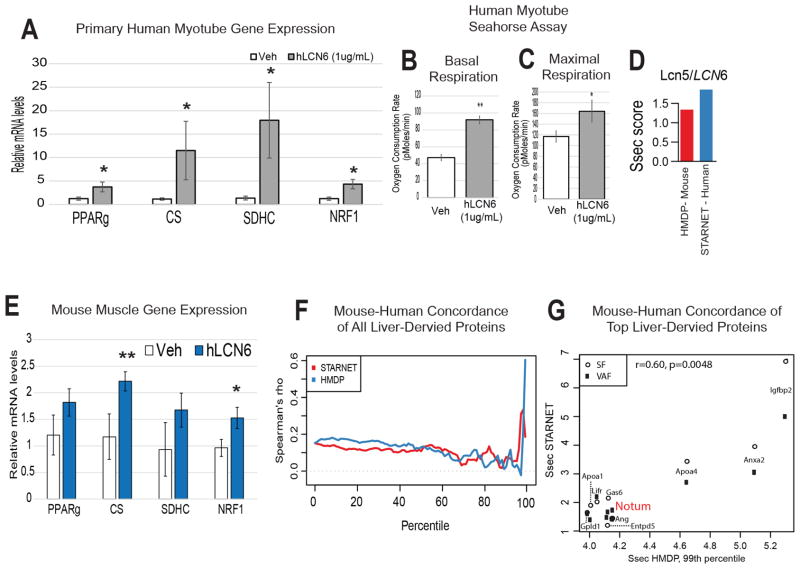
Figure 6. Concordance of mouse and human data using the QENIE pipeline.
As discussed in the text, Lcn6 is the predicted functional orthologue of mouse Lcn5. A, Primary human myotubes were treated overnight with PBS (Veh) or LCN6 (1μg/mL) and gene expression was evaluated using qPCR. n = 6 B–C, Primary human myotubes were treated for 30hrs with veh or LCN6 (1ug/mL) then subjected to Seahorse bioanalyzer system, where significantly enhanced basal (B) and maximal (C) respiratory capacity was observed. n = 4 per group. All data presented as mean ± SEM *p<0.05. D, Ssec scores for both mouse LCN5 (red) and human LCN6 in HMDP and STARNET, respectively. E, Gene expression from gastrocnemius in mice 8 hours after injection of PBS (veh) or 0.1ug/gram body weight recombinant human LCN6. N = 6. F, Spearman’s rho correlation between Ssec of all mouse and human orthologous peptides (y-axis) as a measure of Ssec score percentile within each dataset (x-axis) originating from liver. Note the sharp increase in rho at the tail end of the percentile distribution. G, The top 1% of the HMDP genes from were correlated against their Ssec in STARNET from liver across either visceral (VAF, black squares) or subcutaneous (SF, open circles) fat, with NOTUM highlighted in red.