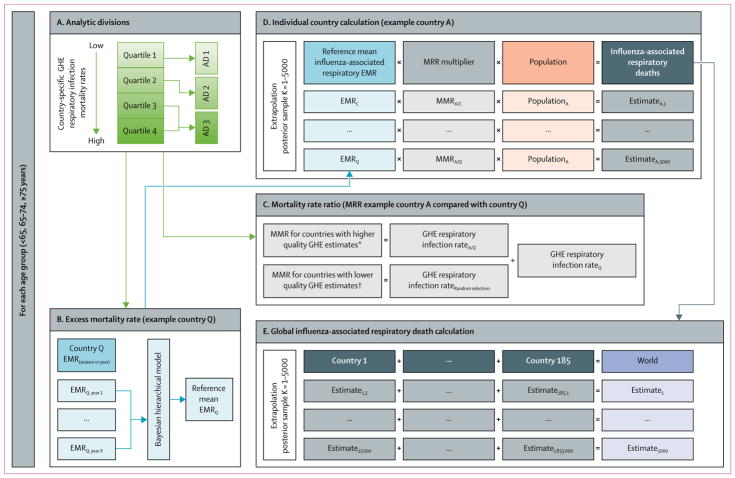
Figure 1. Extrapolation model approach for individual country and global estimates of influenza-associated respiratory deaths.
Country refers to WHO member states, Hong Kong, Taiwan, or regions within a country. WHO GHE were used to categorise countries into ADs and in the extrapolation model. Usability was defined using the following equation: usability (%)=completeness of death registration data (%) × (1–proportion of ill-defined death registration data). AD=analytic division. EMR=excess mortality rate. MMR=mortality rate ratio. GHE=Global Health Estimates. *Countries with at least 5 years of death registration data available (starting from 2005) with a mean usability of all available years (from 2000 onwards) of 60% or more if International Classification of Diseases-coded registration data for specific causes of death were reported, or with a mean usability of 80% or more if only summarised causes of death data were reported. †Countries with no annual death registration data available or countries with less than 5 years of death registration available (starting from 2005) with a mean usability of all available years (from 2000 forward) of less than 60% if International Classification of Diseases-coded registration data for specific causes of death were reported, or a mean usability of 80% or less if only summarised causes of death data were reported.