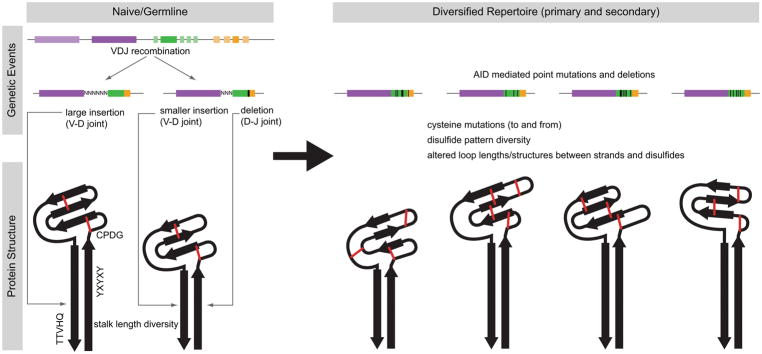
Figure 8. Genetic and structural model for ultralong CDR H3 antibody repertoire formation.
One or more germline V-D-J recombination events using IGHV1-7 (dark purple), IGHD8-2 (dark green), and IGHJ2-4 (dark orange) is shown in the upper left. Junctional diversity, including insertions and deletions, can potentially alter the length of the stalk, as the V-D and D-J joints occur in regions encoding the ascending and descending strands, respectively. Presumably, two disulfide bonds can form in the knob of the naïve/germline antibody (shown in red). The primary repertoire is further diversified in the gut associated lymphoid tissue by AID-mediated processes (upper right). Nucleotide changes that alter amino acid content, particularly to cysteines, can change disulfide patterns and loops (red lines). Larger deletions (black rectangles) in the DH region can also potentially change loop lengths and disulfide patterns. The β-strands of the knob core and stalk domain are represented by black arrows.