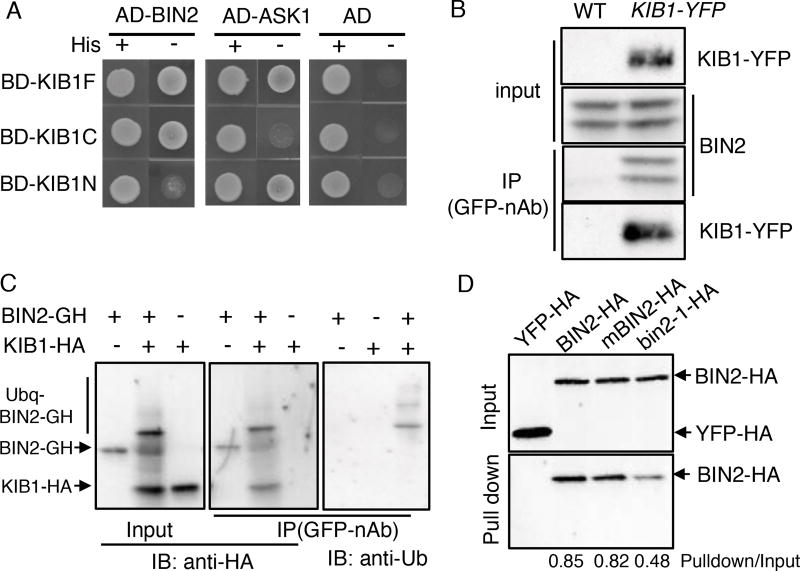
Figure 5. KIB1 interacts with BIN2 and promotes BIN2 ubiquitination.
(A) Yeast-two-hybrid assay shows the interaction between the fragments of KIB1 and BIN2 or ASK1. KIB1F, full-length KIB1; KIB1N, amino acid 1–70; KIBC, amino acid 71–382.
(B) Co-immunoprecipitation assay shows KIB1 is associated with BIN2 in vivo. Total proteins extracted from WT or KIB1::KIB1-YFP transgenic plants were immunoprecipitated with the GFP-nAb, and then probed with the anti-GFP or anti-BIN2 antibody.
(C) In vitro ubiquitination assays show KIB1 promotes BIN2 ubiquitination. BIN2-GFP-HA (BIN2-GH) was incubated with or without KIB1-HA for the ubiquitination assay reactions. The BIN2-GFP-HA protein was immunoprecipitated using the GFP-nAb, and then analyzed by immunoblots using the anti-HA and anti-Ub antibody separately.
(D) In vitro pull-down assays show KIB1 binds to BIN2. BIN2, BIN2Y200F (mBIN2) and bin2-1 fused with HA tags were pulled down by KIB1-YFP-HA immobilized on the GFP-nAb magnetic agarose beads and immunoblotted using an anti-HA antibody. YFP-HA was used as a negative control. The numbers below the blots indicate the ratio of the relative density between pull-down and input signals (Pulldown/Input).
Also see Figure S6.