Figure 1.
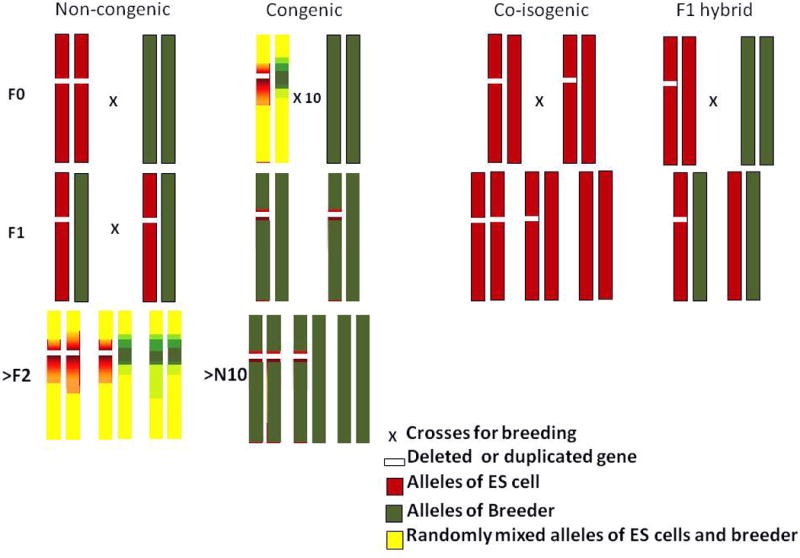
Genetic background of different breeding strategies.
The targeted gene (white band) is shown with background alleles originating from the embryonic stem (ES) cell donor strain (red), a breeder (green), and randomly mixed alleles of both parents (yellow) in non-congenic mice, congenic mice, co-isogenic mice and F1 hybrid mice. Non-congenic wild-type and mutant mice systematically differ in alleles flanking the targeted gene at the F2 generation due to recombination of alleles. By backcrossing such a mouse to the breeder for more than 10 generations (>10N), the genetic background of a congenic mouse is saturated with alleles of the breeder, thereby minimizing the systematic difference in the flanking regions between wild-type and mutant mice. A co-isogenic mouse is developed in ES cells of a mouse strain and bred with the same mouse line. The F1 hybrid is made by crossing a co-isogenic mutant mouse is crossed with another inbred mouse and the identical genetic background is present between wild-type and mutant mice at the F1 generation.
