Figure 2. Point mutations of key residues at the EZH2-SRM/SET-I or EZH2-SRM/EED interface affect global H3K27me2/3 levels in vivo.
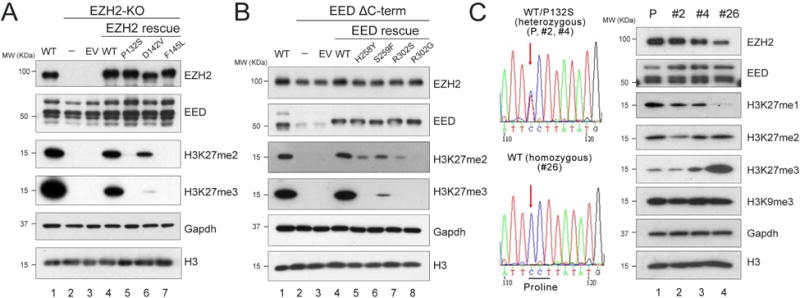
(A-B) Western blot analysis of EZH2, EED, H3K27me2, H3K27me3 and total histone H3 levels in E14 mESC cells, including WT, EZH2-KO, and EZH2 rescue conditions (A) or EEDΔC-term and EED rescue conditions (B). Gapdh was used as a loading control. mESC, mouse embryonic stem cells. EV, empty vector. EEDΔC-term, EED C-terminal deletion.
(C) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated reversal of EZH2P132S to EZH2WT in COLO-679 melanoma cells. Left, Sanger sequencing results for the parental (P) COLO-679 cell line (EZH2WT/P132S), the negative CRISPR clones (EZH2WT/P132S; clones #2 and #4), and the positive CRISPR clone (EZH2WT/WT; clone #26). Right, Western blot analysis of EZH2, EED, H3K27me1, H3K27me2, H3K27me3, H3K9me3 and total histone H3 levels in the parental COLO-679 cells as well as CRISPR clones #2, #4, and #26. Gapdh was used as a loading control.
