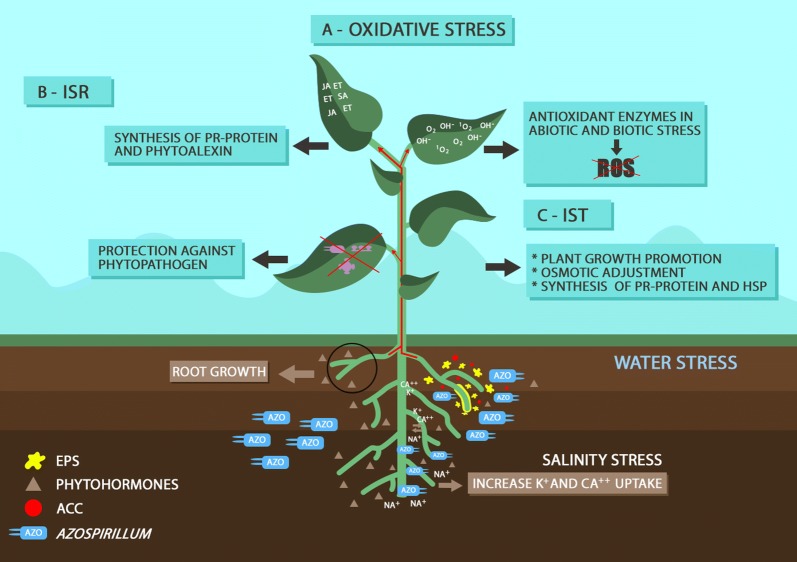
Fig. 1.
Mechanisms of tolerance of biotic and abiotic stresses induced by Azospirillum in plants. Tolerance to biotic stress include induced systemic resistance (ISR), mediated by increased levels of phytohormones in the jasmonic acid (JA)/ethylene (ET) pathway independent of salicylic acid (SA), and systemic acquired resistance (SAR)—a mechanism previously studied with phytopathogens—controlled by intermediate levels of SA. Tolerance of abiotic stresses, named as induced systemic tolerance (IST), is mediated by antioxidants, osmotic adjustment, production of phytohormones, and defense strategies such as the expression of pathogenesis-related (PR) genes