Fig. 1.
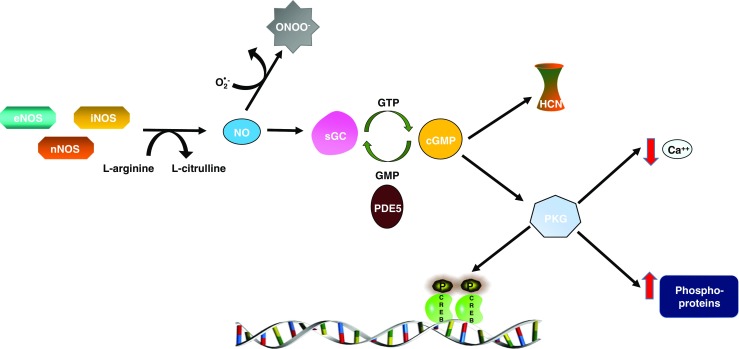
Nitric oxide synthesis and signaling. The three NO synthases: nNOS, eNOS, and iNOS produce NO through the oxidation of L-arginine. Soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) is the high affinity receptor for NO in the body. Upon binding of NO, sGC converts guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which in turn activates the cell membrane bound ion channels; hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide–gated channel (HCN), and cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG). PKG regulates a number of proteins through phosphorylation, and the results include altered gene expression, decreased intracellular calcium, and modified G protein coupled receptor activation [3]. Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) specifically breaks down cGMP to GMP, thus acting as a negative regulator of this pathway
