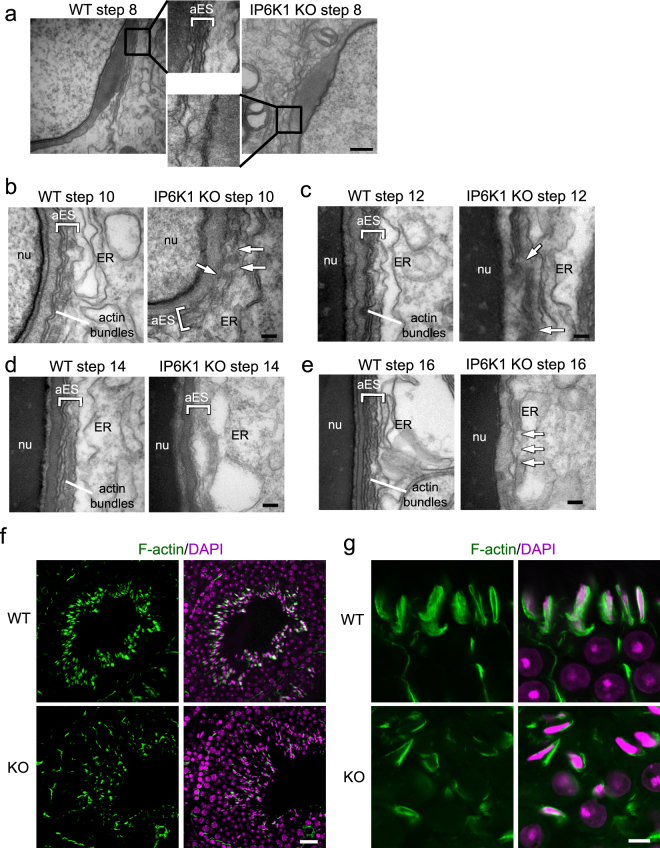
Figure 7.
IP6K1 deletion disrupted apical ectoplasmic specialization. (a–e) Evaluation of spermatids by electron microscopy. (a) No characteristic apical ectoplasmic specialization (aES) was observed in step 8 spermatids of IP6K1 KOs (inset). Scale bar 500 nm. (b) The aES was not well formed in step 10 spermatids of IP6K1 KOs (arrows). ER: endoplasmic reticulum; nu: nucleus. Scale bar 100 nm. (c) Disorganized aES was seen in step 12 spermatids of IP6K1 KOs (arrows). ER: endoplasmic reticulum; nu: nucleus. Scale bar 100 nm. (d) Apical ES was collapsing in step 14 spermatids of IP6K1 KOs. ER: endoplasmic reticulum; nu: nucleus. Scale bar 100 nm. (e) Apical ES collapsed in step 16 spermatids of IP6K1 KOs (arrows). ER: endoplasmic reticulum; nu: nucleus. Scale bar 100 nm. (f and g) The actin surrounding spermatids were decreased in IP6K1 KOs. Staining of F-actin by phalloidin on seminiferous tubules. Scale bar 20μm in (f); scale bar 5μm in (g).