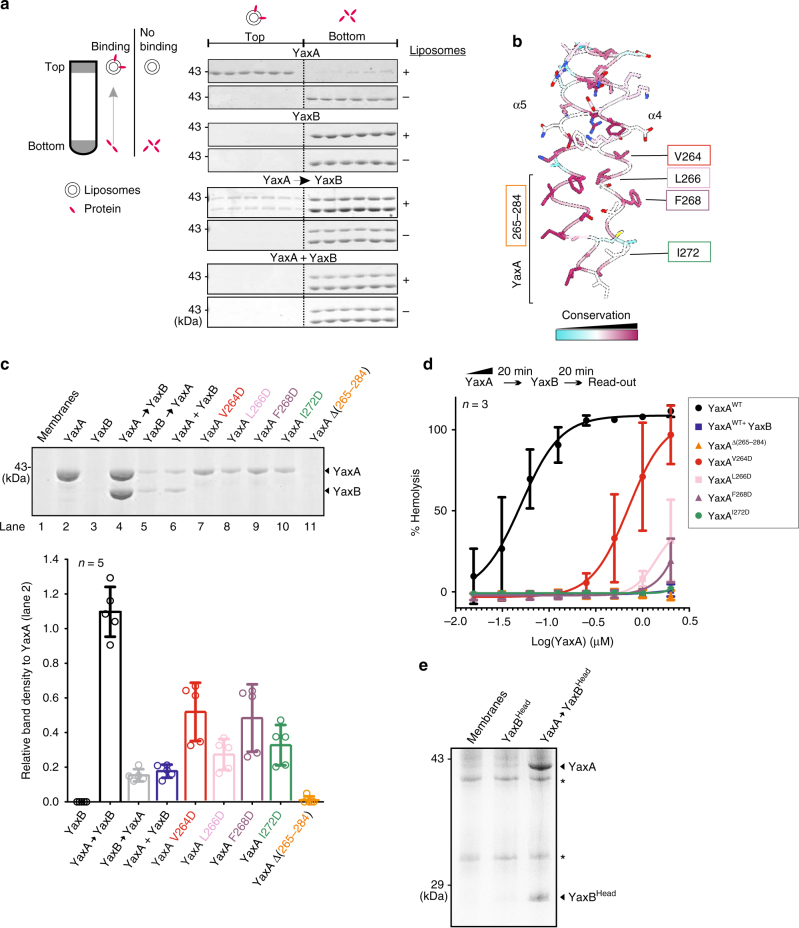
Fig. 6.
YaxA binds to membranes via its foot domain and recruits YaxB through the head domain. a Liposome floatation assay to test membrane-binding abilities of YaxA and YaxB. Left: schematic presentation of the experiment. Right: membrane binding of i) YaxA, ii) YaxB, iii) sequentially added YaxA and YaxB (YaxA → YaxB) and iv) pre-mixed YaxA and YaxB (YaxA + YaxB) assessed by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE analysis of top and bottom gradient fractions. For each sample, a control run was performed without liposomes. Representative data shown are from one experiment repeated twice. Only a fraction of protein in the YaxA → YaxB sample floated to the top of the gradient in the same time frame, likely reflecting the different behavior of pore-decorated liposomes compared with those bound to YaxA alone. b Close-up view of YaxA’s surface-hydrophobic foot domain. Residues targeted for mutation are indicated; a bracket delineates the hydrophobic foot, encompassing residues 265–284. c Erythrocyte membrane co-sedimentation assay of WT and mutant YaxA. Top: for each condition, trypsinized erythrocyte ghosts were incubated with the respective toxin component, sedimented, and analyzed by Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE. Bottom: YaxA band intensities relative to the YaxA-only sample (lane 2) were determined densitometrically from the SDS-PAGE scans (Supplementary Figure S15). Data points from five independent experiments (n = 5) are shown, along with their means and corresponding standard deviations (SD). d Erythrocyte hemolysis assay of WT and mutant YaxA. Erythrocytes were treated first with serial dilutions of WT YaxA or its mutants, followed by YaxB addition. In case of pre-mixed YaxAB, buffer was added for the second incubation step. Hemoglobin release was read at 413 nm and normalized against complete hemolysis by 1% Triton X-100 (100% hemolysis) or a buffer control (0% hemolysis). For each YaxA concentration, the average from three independent experiments (n = 3) is presented along with the standard deviation; solid lines correspond to the the fitted dose-response curves. e Membrane co-sedimentation assay (conducted as in c), demonstrating the ability of membrane-bound YaxA to recruit the isolated YaxB head domain to membranes. Membranes were not trypsinized beforehand; hence protein contaminants (asterisks) are present