Figure 3.
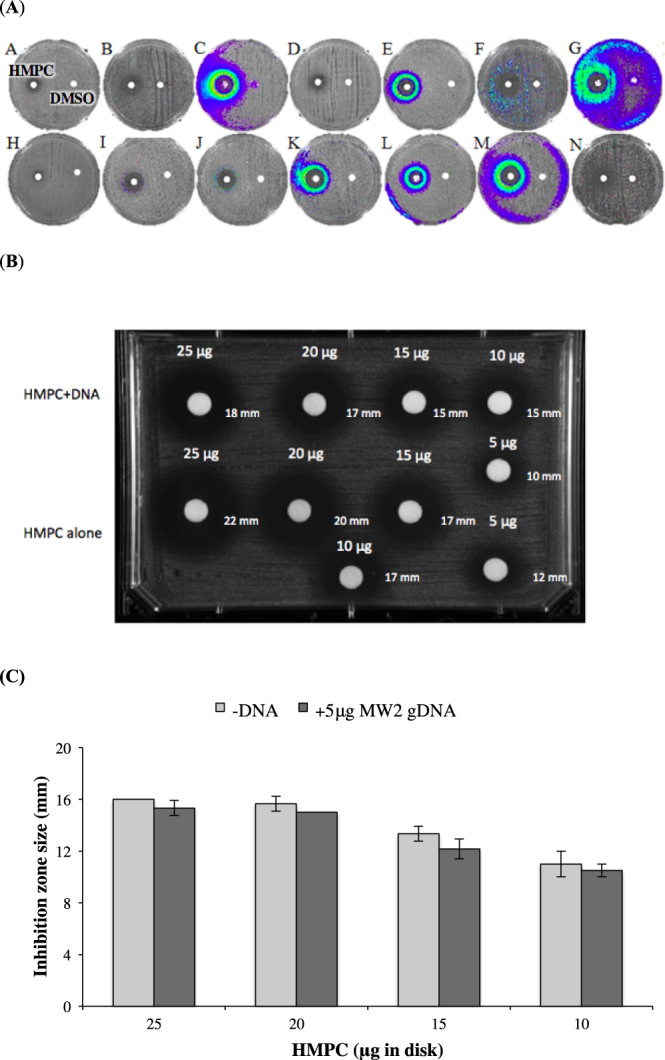
Response of the S. aureus promoter-lux array to HMPC treatment. (A) Results of promoter-lux array screening. The name of each reporter clone is shown in the upper left corner of each picture. A clear zone around the disc indicates inhibition of growth in the presence of higher concentrations of HMPC. At the periphery of the inhibition zone, where sub-MIC levels of HMPC are present, changes in luminescence indicate altered transcription. The disc on the left is HMPC and on the right of each panel is a DMSO (vehicle) control. (B) Zones of S. aureus growth inhibition produced by HMPC in the presence or absence of calf thymus DNA. Decreasing quantities of HMPC (25–5 μg) were incubated with either 5 μg calf thymus DNA or TE buffer (control) before being spotted onto discs and placed onto agar plates containing S. aureus MW2 bacterial lawns. (C) Disc diffusion assay with varying concentrations of HMPC in the absence or presence of S. aureus genomic DNA. HMPC was incubated without or with 5 μg of S. aureus genomic DNA and was then applied to a filter paper disc and placed onto a TSA plate containing S. aureus MW2 bacteria in a soft agar overlay. After overnight incubation at 37 °C, zones of inhibition were measured with a ruler. Bars show mean values +/− standard deviation of three independent assays, and no differences are statistically significant.
