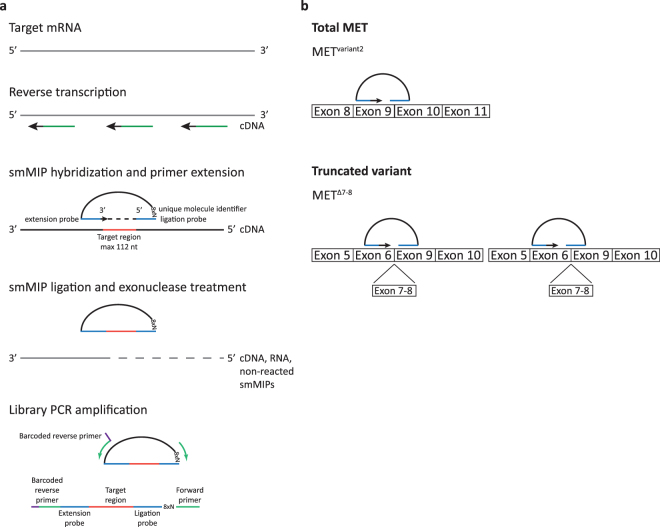
Figure 1.
Quantitative detection of transcript splice variants using smMIPs. (a) Schematic overview of the method. mRNA is reverse transcribed into cDNA using random primers. SmMIP probes hybridize to the target region of interest, leaving a gap of ~112 nucleotides. The gap is filled by primer extension and ligation, whereafter all remaining linear smMIPs, RNA and cDNA are removed by exonuclease treatment. All circular smMIPs are PCR amplified using a unique barcoded reverse primer for each sample. Resulting reads are mapped against reference transcriptomes, normalized to the total read count within a sample (FPM), and averaged per transcript variant. (b) Design of smMIP probes. To determine the total expression of a gene, smMIPs were designed against shared parts of the transcript of interest (upper panel). For specific detection of splice variants smMIPs were designed to target variant-specific exon-exon junctions (for example the exon6–9 junction for METΔ7-8), either covering the junction with the gap or the ligation/extension probe (lower panel left and right, respectively). Note that for graphical representation, the figure is not to scale.