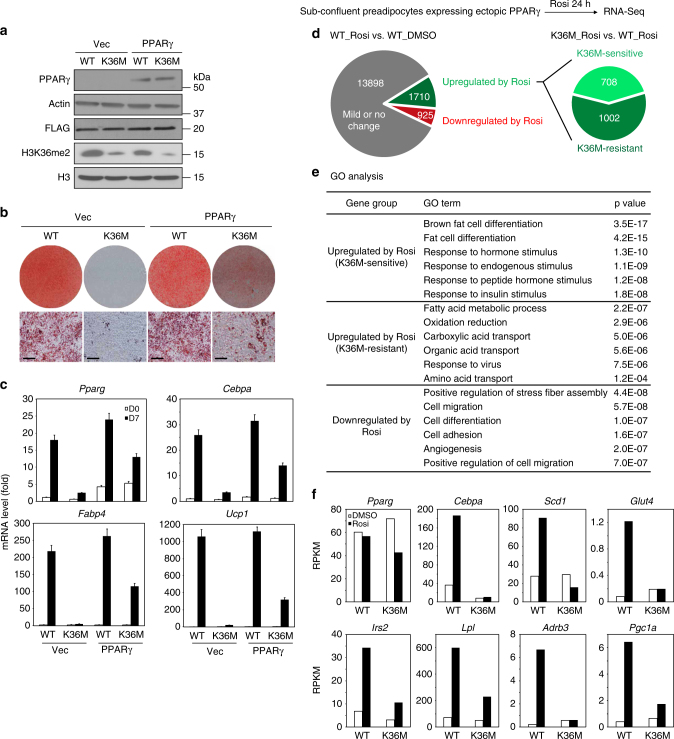
Fig. 2.
H3.3K36M inhibits ligand-induced PPARγ target gene expression. Immortalized brown preadipocytes were infected with retroviral vector expressing FLAG-tagged WT or K36M mutant histone H3.3. After puromycin selection, cells were infected with retroviral vector expressing PPARγ or empty vector, followed by hygromycin selection. a Western blot analysis in preadipocytes using antibodies indicated on the left. b Oil Red O staining at D7 of adipogenesis. Scale bars = 30 μm. c qRT-PCR of Pparg, Cebpa, Fabp4, and Ucp1 expression at D0 and D7 of adipogenesis. qRT-PCR data are presented as means ± SEM. Three technical replicates from a single experiment were used. d–f Sub-confluent preadipocytes expressing ectopic PPARγ were treated with DMSO or 0.5 μM PPARγ ligand Rosiglitazone (Rosi) for 24 h, followed by RNA-Seq analysis. d Schematic of identification of K36M-sensitive and K36M-resistant genes up-regulated by Rosi treatment. The threshold for up-regulation or down-regulation is twofold. e GO analysis of gene groups defined in d. f RPKM values of Pparg and representative PPARγ target genes from RNA-Seq analysis