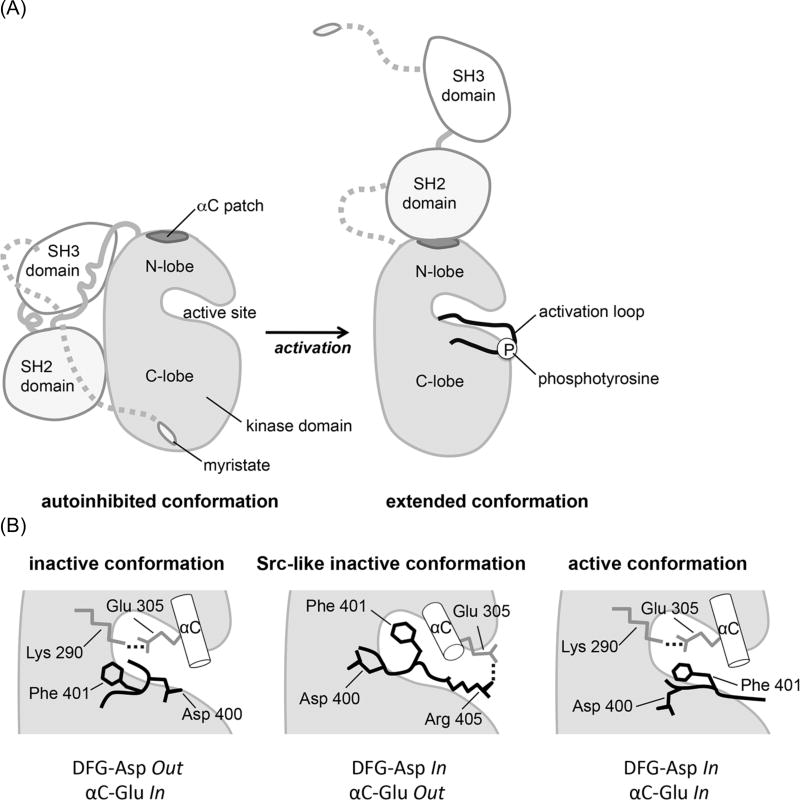
Figure 1. Conformational states of c-Abl.
(A) Schematic depicting two distinct domain arrangements in the autoinhibited and active states of c-Abl. In the autoinhibited, assembled state the N-terminal myristoyl group binds to the kinase domain and allows the SH2 and SH3 domains to dock onto it [2,40]. Open autoinhibited conformations also exist [5]. In the extended, active conformation, the SH2 domain forms an interface with the N-lobe of the kinase domain, involving the αC patch and Tyr 412 in the activation loop undergoes rapid autophosphorylation.
(B) Schematic representation of critical components of the active site in various states of the Abl kinase domain: the inactive conformation as seen in the complex with imatinib, the Src-like inactive conformation, and the active conformation. The DFG motif at the base of the activation loop and αC helix are shown. Ionic interactions are indicated as dotted lines.