Fig. 7.
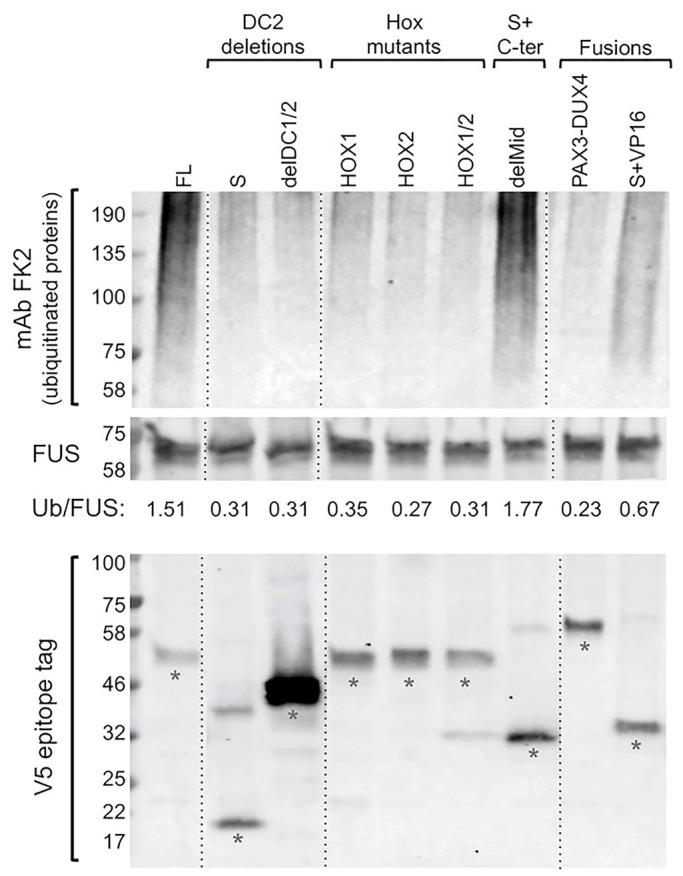
Increased protein ubiquitination induced by DUX4-FL, delMid, and S+VP16 proteins. Upper panel: HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated DUX4 constructs, and the level of protein ubiquitination was determined by immunoblotting with mAb FK2 at 48 h after transfection. Middle panel: immunostaining for the protein FUS, which was unaffected by the transfected plasmids, served as a loading control. The ratio of ubiquitinated proteins to FUS (Ub/FUS) was determined by densitometry with ImageJ. As in our previous work (Homma et al., 2015), expression of DUX4-FL (FL), but not DUX4-S (S), increased the level of protein ubiquitination. Ubiquitination was also increased by expression of the delMid protein and, to a lesser extent, by the S+VP16 fusion protein, whereas ubiquitination was not affected by the other tested constructs. Thus, the three proteins with greatest effect in other assays (see Fig. 6) also had the greatest effect on protein ubiquitination. Lower panel: an immunoblot of the V5-tagged proteins produced from each transfected plasmid showed that each construct produced a major band (denoted by asterisks) that was of the appropriate predicted size. Though most of the tested constructs generated about the same level of V5-tagged protein (indicating that lack of effect on ubiquitination was not due to lack of expression), the delDC1/DC2 construct generated more protein than the other constructs, a result consistent with the finding of Bosnakovski et al. (2017a) that deletion of C-terminal regions increases DUX4 accumulation in transfected cells. All samples in each panel were from the same blot, but lanes were re-arranged (as indicated by the dotted lines) for presentation.
