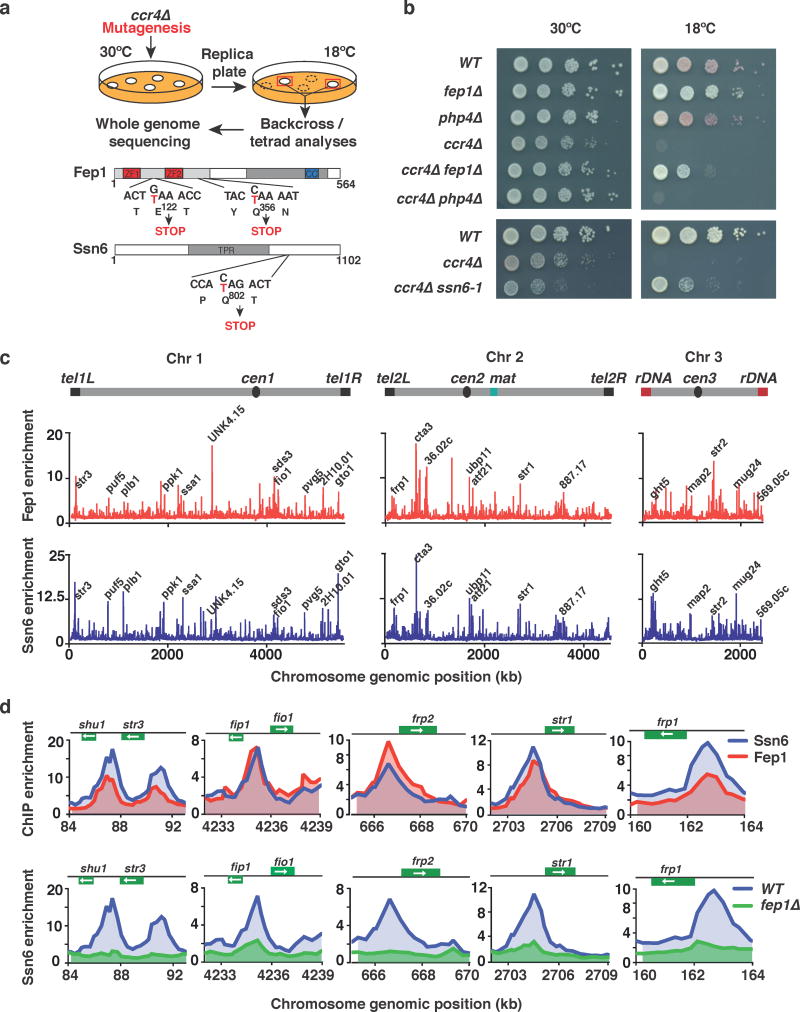
Figure 4. Mutation of fep1 or ssn6 restores growth in ccr4Δ cells at 18°C.
(a) Genetic screen for suppressors of the cold-sensitive growth phenotype of ccr4Δ cells. Cells were mutagenized by UV irradiation and suppressors were isolated. Mutants were backcrossed to WT, and the phenotype was tracked in ccr4Δ cells by assaying growth at 18°C. Whole genome sequencing and nucleotide variant analysis identified two independent suppressor mutations in fep1 (fep1-1 E122→STOP and fep1-2 (Q365→STOP), as well as a suppressor mutation in ssn6 (ssn6-1 Q802→STOP). (b) Serial dilutions of the indicated strains were spotted onto rich media (YEA) and incubated at 30°C for 3 days, or 18°C for 11 days. (c) ChIP-chip analysis of genome-wide Fep1-GFP (upper) or Ssn6-Myc (lower) relative enrichment in cells grown at 30°C. Iron transporter loci and other peaks are indicated. (d) ChIP-chip analysis of Fep1-GFP and Ssn6-Myc relative enrichment (upper) or Ssn6-Myc relative enrichment at iron transporter genes in WT or fep1Δ cells (lower) grown at 30°C.