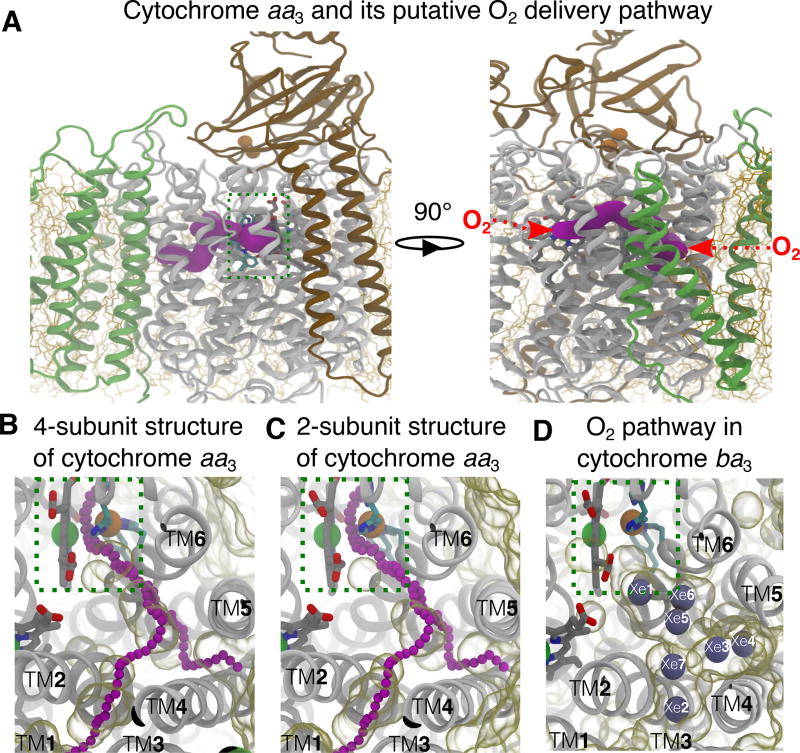
Figure 1.
Putative O2 delivery pathway in HCOs. A) Location of the pathway in cytochrome aa3. The R.s. enzyme comprises four subunits: SI (white), SII (brown), SIII (green) and SIV (not shown). SI and SII are the minimal functional units of HCOs. The O2 reduction site is highlighted using a dashed green box. The X-ray inferred pathway, located in SI, is shown in magenta surface drawn using CAVER 3.0.47 This structural model is from PDB 1M56.13 Red arrows on the right panel depict the entrances of the pathway. B–C) Projected from the top view, the putative O2 pathway in cytochrome aa3 is illutrated by chains of magenta balls drawn by CAVER3.0. Unoccupied spaces within the protein were visualized using the molecular surface representation in VMD with the probe radius of 1.7 Å, which is about the vdW radius of an oxygen atom. Comparison between the crystal structure with 4 subunits (B) and the one with only SI and SI subunits from PDB 2GSM14 (C) indicates that SIII does not block the TM4–5 entrance. The simulations were performed using the 2-subuit structure. D) The equivalent pathway in cytochrome ba3 was found to bind Xe (gray balls) by X-ray crystallographic experiments24,25 and characterized as the O2 delivery pathway in MD simulations.1 The structural model is from PDB 1XME27 and the atom coordinates of Xe are from PDB 3BVD.24 The Xe atoms are numbered according to Luna et al.24