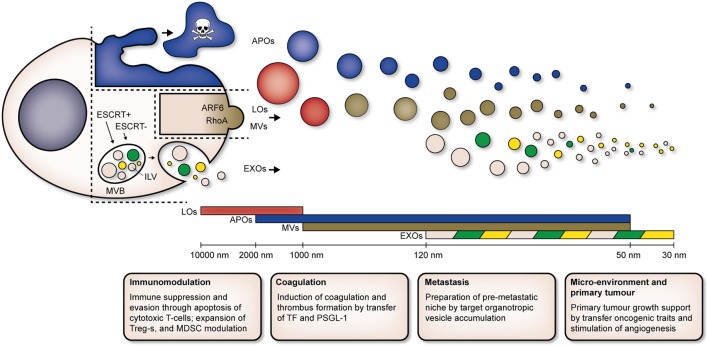
Figure 1.
Cells release heterogeneous populations of EVs with overlapping sizes. APOs (blue) are released by cells undergoing apoptosis. LOs (red) and MVs (brown) are derived directly from the plasma membrane, ARF6 and RhoA are key players in biogenesis of MVs. EXOs (pink) are derived from intracellular endosomal compartments. ILVs form within MVBs and are subsequently released upon fusion of MVBs with the plasma membrane. Both ESCRT-dependent (ESCRT+) and -independent (ESCRT−) pathways are involved in biogenesis of EXOs. Unique subpopulations of EXOs (as indicated by green and yellow EVs) have been identified. Abbreviations: MVB, multivesicular body; ILV, intraluminal vesicle; ESCRT+, endosomal sorting complex required for transport-dependent; ESCRT, endosomal sorting complex required for transport-independent; ARF6, ADP-ribosylation factor 6; RhoA, Ras homolog gene family, member A; EVs, extracellular vesicles; APOs, apoptotic bodies; LOs, large oncosomes; MVs, microvesicles; EXOs, exosomes; Tregs, T regulatory T cells; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; TF, tissue factor; PSGL-1, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1.