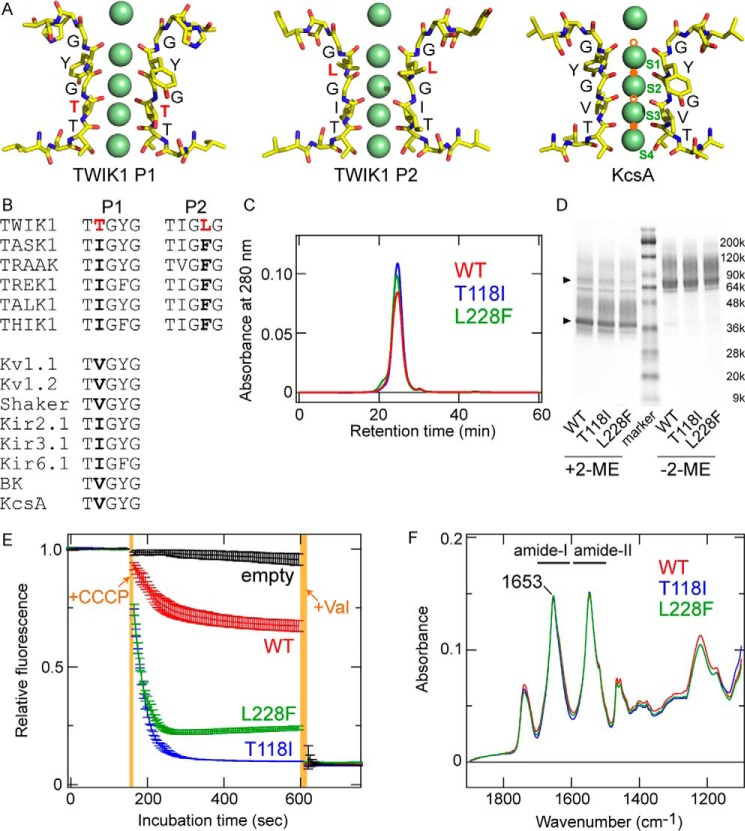
Figure 1.
Molecular characteristics of TWIK1. A, comparison of atomic models of the selectivity filter for TWIK1 (PDB code 3UKM) and KcsA (PDB code 1K4C). Green spheres indicate K+ ions resolved in the crystal structures. The K+-binding sites, S1–S4, are labeled in the KcsA structure. Note that the structural models were constructed from the averaged electron density maps, and all of the K+ ions do not exist simultaneously (2). The pore domains (P1 and P2) in TWIK1 possess unique filter residues, Thr-118 and Leu-228, respectively. In the KcsA structure, Na+/Li+-binding sites (B-sites) are indicated by orange circles. The lower filled orange circle indicates the Li+-binding site (4) as well as a potential Na+-binding site (5, 6), and the upper filled orange circle indicates the Na+-binding site (5). Open orange circles are hypothetical binding sites for Na+/Li+ (6). B, amino acid sequence alignment in the selectivity filter of K+ channels. A and B, unique residues Thr-118 and Leu-228 are highlighted in red. C, size-exclusion chromatographs of purified TWIK1: WT (red), T118I mutant (blue), and L228F mutant (green). D, Coomassie Brilliant Blue-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel with purified WT TWIK1 and mutants (T118I and L228F) in the presence (+2-ME) or absence (−2-ME) of a reducing reagent (final concentration of 5% 2-mercaptoethanol (2-ME)). The triangles indicate major bands of the purified TWIK1 samples with or without reduction. E, traces of flux assay fluorescence changes using liposomes containing TWIK1: WT (red), T118I mutant (blue), or L228F mutant (green) and “empty” liposomes without channel proteins (black). Error bars indicate S.D. values from three independent measurements. +CCCP indicates the time point of addition for the CCCP protonophore, and +Val indicates the time point of addition for the K+-selective ionophore valinomycin. Orange-shaded areas indicate the dead time for adding and mixing CCCP or valinomycin. F, absolute IR absorption spectra of WT (red), T118I (blue), and L228F (green) after normalization at the amide-I peak (at 1653 cm−1).