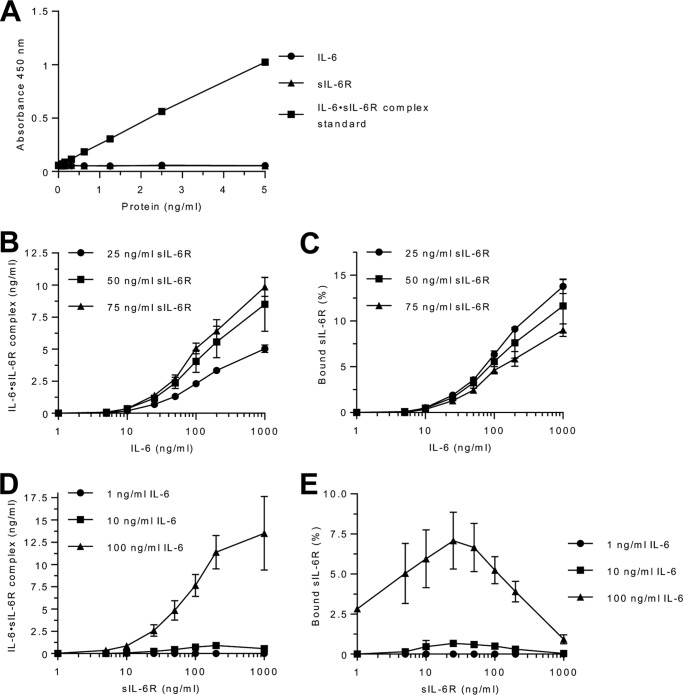
Figure 1.
Quantification of IL-6·sIL-6R complexes. A, validation of the IL-6·sIL-6R ELISA was performed with recombinant IL-6 (0.078–5 ng/ml), sIL-6R (0.078–5 ng/ml), or the IL-6·sIL-6R complex standard (0.078–5 ng/ml). B, recombinant human IL-6 (1–1,000 ng/ml) and sIL-6R (25, 50, or 75 ng/ml) were mixed and IL-6·sIL-6R complexes were quantified by IL-6·sIL-6R ELISA. Combined data from three experiments are shown. Error bars represent the S.D. C, the percentages of sIL-6R present in IL-6·sIL-6R complexes were calculated from B. The calculation is based on the molecular masses of IL-6 (23.7 kDa) and sIL-6R (51.5 kDa), bound in the IL-6·sIL-6R complex (75.2 kDa, ratio = ∼1/3 IL-6 and 2/3 sIL-6R). For example, 5 ng/ml of IL-6/sIL-6R were detected, by combination of 100 ng/ml of IL-6 and 50 ng/ml of sIL-6R. Thus the complex consists of 3.42 ng/ml of sIL-6R and 1.58 ng/ml of IL-6. Consequently, 6.85% of the used sIL-6R and 1.57% of the used IL-6 were bound in the IL-6·sIL-6R complex. Error bars represent the S.D. D, recombinant human sIL-6R (1–1,000 ng/ml) and IL-6 (1, 10, or 100 ng/ml) were mixed and IL-6·sIL-6R complexes were quantified by IL-6·sIL-6R ELISA. Combined data were from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the S.D. E, the percentages of sIL-6R present in IL-6·sIL-6R complexes were calculated from D.