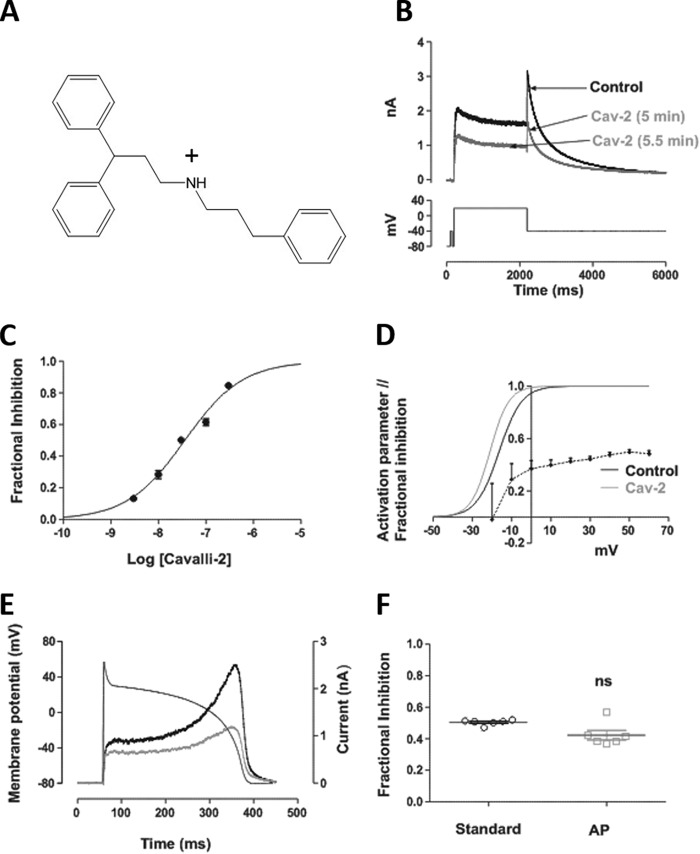
Figure 2.
Effect of Cavalli-2 on WT IhERG. A, structure of the “minimally structured” compound Cavalli-2. B, upper panel, shows representative traces recorded in 4 mm normal [K+]e elicited by depolarizing voltage command (lower panel) in the absence (black) and presence (gray) of 30 nm Cavalli-2 (Cav-2) after 5 and 5.5 min to demonstrate steady-state block. C, concentration-response relationships for inhibition of IhERG tails at −40 mV by Cavalli-2 (n ≥ 5 for each point). D, voltage dependence of Cavalli-2 block (black dotted line) and voltage-dependent activation relationships for IhERG in control (black continuous line) and in the presence of 30 nm Cavalli-2 (gray line) (n = 6). V0.5 = −16.0 ± 3.6 mV and k = 5.37 ± 0.75 and V0.5 = −21.2 ± 2.9 mV and k = 5.03 ± 1.50 in control and in the presence of 30 nm Cavalli-2, respectively. E, representative IhERG records in control (black) and in the presence of 30 nm Cavalli-2 (red line) elicited by the superimposed action potential waveform. F, scatter plot comparing fractional block of IhERG by 30 nm Cavalli-2 using the standard protocol and action potential waveform. n = 6; p < 0.05, unpaired t test. Error bars represent means ± S.E. ns, not significant.