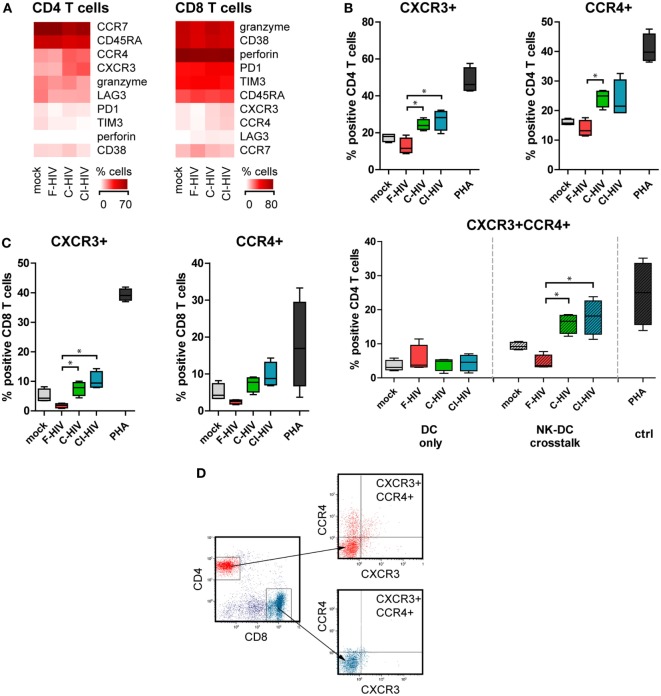
Figure 7.
T cell phenotype activated by natural killer (NK)–dendritic cell (DC) stimulation assay. DCs and NK cells from the same donor were cocultured and exposed to 1 μg/ml F-HIV, complement-opsonized HIV (C-HIV), complement- and antibody opsonized HIV (CI-HIV), PHA, or mock treated for 24 h. The experiment was replicated four times using cells derived from four different donors. Allogeneic T cells were then added to the cultures at a 1:10 DC:T cell ratio. (A) The T cell phenotype induced was assessed by flow cytometry. Heat maps of the percentage of CD4 and CD8 cells positive for phenotypic markers were created. (B) The number of CD4 T cells positive for CXCR3 or CCR4 were evaluated in culture with DCs conditioned with NK cells, and the number of CD4 T cells positive for both CXCR3 and CCR4 were evaluated in culture with DCs conditioned with NK cells or DCs alone. (C) The number of CD8 T cells positive for CXCR3 and CCR4 was evaluated in culture with DCs conditioned with NK cells. (D) Gating strategy for flow cytometry analysis of a representative sample can be seen. Boxplots show mean with Tukey error bars. One-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni posttest was used to test for statistical significance (*p < 0.05, N = 4).