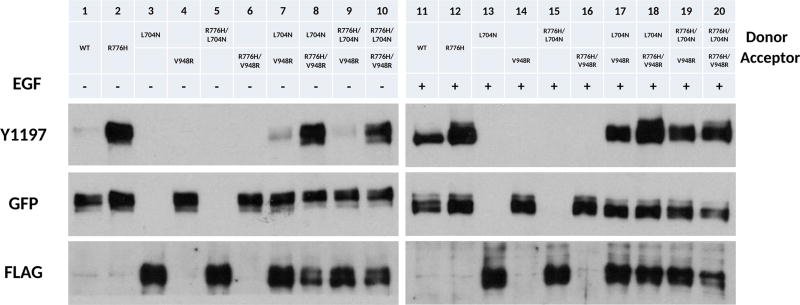
Figure 2.
R776H is a “superacceptor”. + and − indicate the presence and absence of EGF ligand, respectively. Lanes from left to right, WT EGFR (−), R776H (−), L704N (−), V948R (−), R776H/L704N (−), R776H/V948R (−), L704N and V948R (−), L704N and R776H/V948R (−), R776H/L704N and V948R (−), R776H/L704N and R776H/V948R (−), WT EGFR (+), R776H (+), L704N (+), V948R (+), R776H/L704N (+), R776H/V948R (+), L704N and V948R (+), L704N and R776H/V948R (+), R776H/L704N and V948R (+), R776H/L704N and R776H/V948R (+). + and − indicate the presence and absence of EGF ligand, respectively. WT EGFR, R776H, V948R, R776H/V948R are GFP tagged, whereas L704N and R776H/L704N are FLAG tagged.