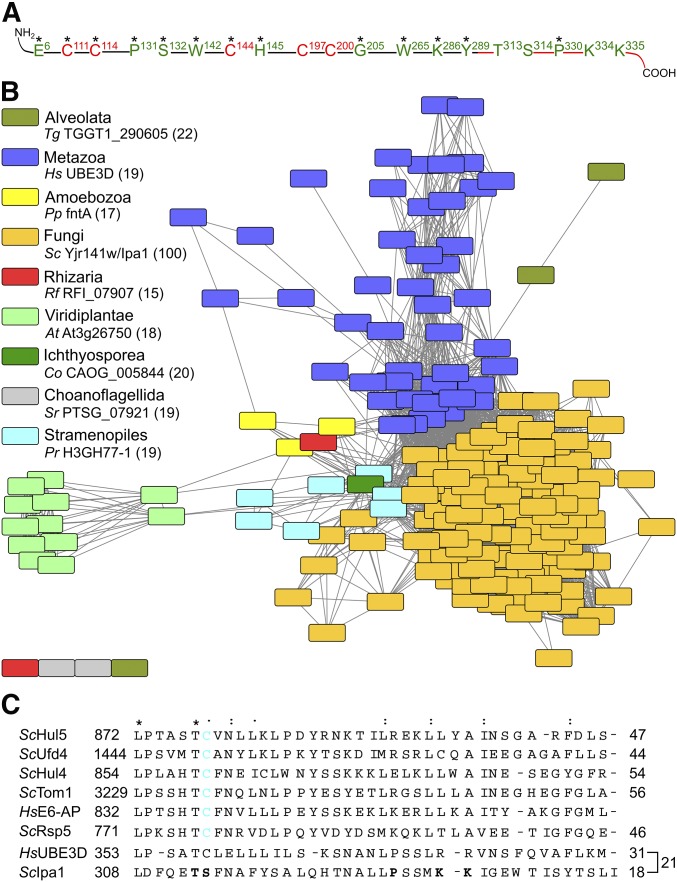
Figure 1.
The yeast protein Yjr141w/Ipa1 belongs to the eukaryotic HECT_2 family. (A) Conserved residues within Yjr141w/Ipa1 match the family signature of HECT_2-family members. Highly conserved residues are marked with an asterisk. Residues or parts of the protein that are essential for Yjr141w/Ipa1 function are marked in red, residues in green are dispensable. (B) Sequence similarity network of HECT_2-family members. Sequences with an identity > 50% were clustered together in one node. The coloring shows affiliation of the protein(s) to one of the eukaryotic subgroups (source: taxonomy database of UniProt). For each subgroup, one protein is given as example; its sequence identity to S. cerevisiae Yjr141w/Ipa1 is given in parentheses. The Pfam identifiers for each node are given in Table S1. (C) Alignment of the C-termini of S. cerevisiae HECT-family members Hul5, Ufd4, Hul4, Tom1, and Rsp5 with the prototype HECT-domain protein human E6-AP and HECT_2-family members Yjr141w/Ipa1 and human homolog UBE3D. The conservation grade of a residue is shown by asterisk, double point, and point to indicate strict conservation, and higher and lower similarity, respectively. The percentage of identical residues between E6-AP and the other sequences is given on the right side as well as the percentage of identical residues between UBE3D and Ipa1. The cysteine residue important for ubiquitylation in HECT domain E3s is highlighted in cyan, residues that have been mutated in Ipa1 to assay for functionality are marked in bold letters. At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Co, Capsaspora owczarzaki; E3, ubiquitin-protein ligase; HECT, homologous to E6-AP carboxyl terminus; Hs, Homo sapiens; Pp, Polysphondylium pallidum; Pr, Phytophthora ramorum; Rf, Reticulomyxa filosa; Sc: S. cerevisiae; Sr, Salpingoeca rosetta; Tg, Toxoplasma gondii.