Figure 6. CSANs Direct Reversible Cell-Cell Interactions.
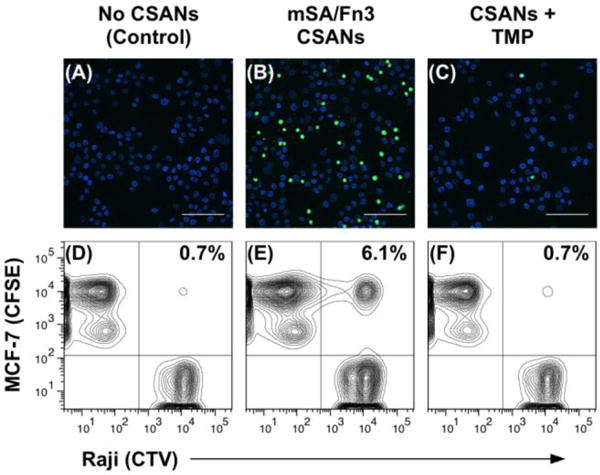
For the fluorescence microscopy experiment (top row), Raji cells were sequentially labeled with CFSE, DSPE-PEG2000-biotin and with or without mSA/Fn3 CSANs; they were then incubated with a monolayer of EpCAM+ MCF-7 cells. (A) In the absence of CSANs, the phospholipid-modified Raji cells are unable to interact with the MCF-7 cells. (B) When functionalized with the mSA/Fn3 CSANs, the EpCAM-targeted Raji cells adhere to the MCF-7 cell monolayer. (C) The EpCAM-targeted Raji cells can be dissociated from the MCF-7 cell monolayer by disassembling the CSAN with trimethoprim (TMP). Scale bars in (a-c) represent 100 μm. For the flow cytometry experiment (bottom row), the target MCF-7 cells were labeled with CFSE while the Raji cells were labeled with CTV. Raji cells were again modified with DSPE-PEG2000-biotin and labeled with or without mSA/Fn3 CSANs. (D) In the absence of CSANs, the phospholipid-modified Raji cells are unable to interact with the MCF-7 cells. (E) When functionalized with the mSA/Fn3 CSANs, the EpCAM-targeted Raji cells formed stable clusters with the MCF-7 cells. (F) The Raji/MCF-7 cell clusters were readily dissociated with trimethoprim. Data are representative of replicate (n = 3) experiments.
