Figure 1. 2i increases acetylation at key pluripotency loci.
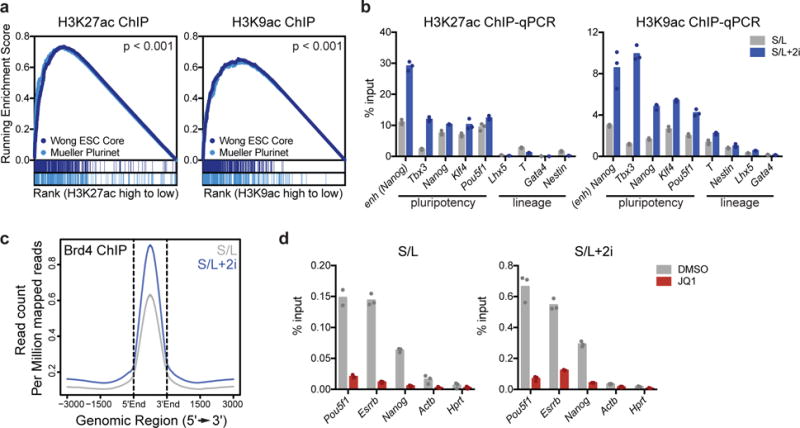
(a) Gene set enrichment plot showing that genes associated with high H3K9ac and H3K27ac are enriched for two independently defined pluripotency gene sets: Muller Plurinet (genes involved in the protein-protein network shared by diverse pluripotent cell types53) and Wong ESC Core (genes coordinately upregulated in mouse and human ESCs54). Data are derived from a single ChIP-Seq experiment26. P values are calculated based on 1000 permutations by the GSEA algorithm and was not adjusted for multiple comparisons. (b) 2i increases acetylation at key pluripotency genes. H3K27ac (left) and H3K9ac (right) at enhancer (enh) or promoters of indicated genes as assessed by ChIP-qPCR. (c) ChIP-seq meta profile for Brd4 binding in ESCs cultured in S/L or S/L+2i. The metaprofile is centered on the midpoint of all Brd4 ChIP-seq peaks. (d) Brd4 ChIP-qPCR illustrating Brd4 binding in ESCs cultured in S/L (left) or S/L+2i (right) treated with DMSO (vehicle) or 500 nM JQ1 for 24 h. (b,d) Bars represent mean of n=3 technical replicates from one IP.
