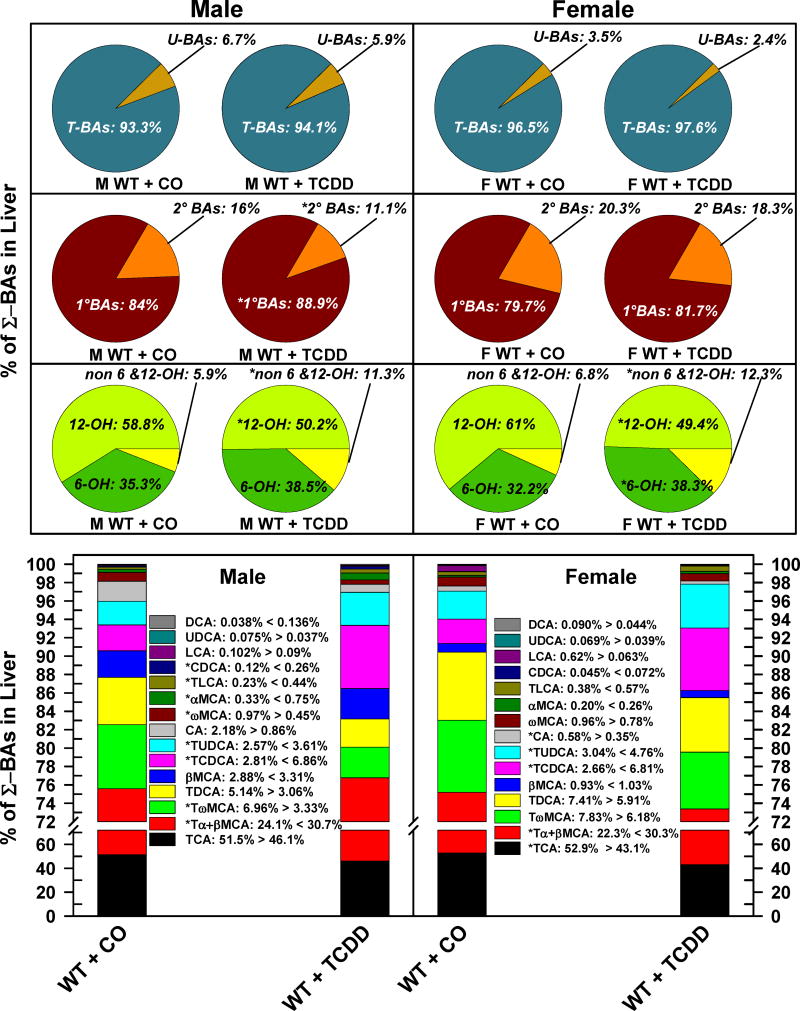
Fig 2.
Effect of TCDD on hepatic composition of individual bile acids in WT male and female mice. Corn oil (vehicle) or TCDD (37 μg/kg) was administered daily (IP) for 4 days to male and female mice (at least 6 mice per treatment group). On the 5th day livers were harvested and the individual BAs were quantified by UPLC-MS/MS. Each section in pie charts and bars was calculated to represent the mean proportion of an individual BA relative to the Σ-BA concentration. Asterisks indicate significant difference (p < 0.05) from the respective value of the WT. Primary bile acids (1°BAs), secondary bile acids (2°BAs), 6-hydroxylated bile acids (6-OH), 12α-hydroxylated (12-OH) bile acids, cholic acid (CA), chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), deoxycholic acid (DCA), females (F), lithocholic acid (LCA), males (M), muricholic acid (MCA), Non-6-, non-12α-hydroxylated bile acids (non-6,12-OH), total bile acids (Σ-BAs), T-conjugated bile acids (T-BAs), 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), unconjugated bile acids (U-BAs), ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), wild-type mice (WT). Color image is available in the online version of the article.