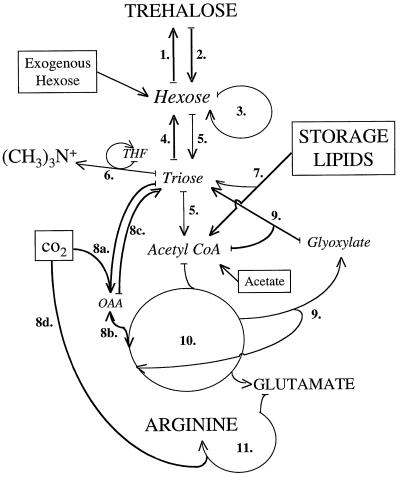
Figure 4.
A simplified scheme of the AM fungal metabolic pathways revealed active in the present study. Labeled substrates provided in different experiments are shown in boxes, products detected are shown in capital letters, and certain metabolic intermediates or pools whose presence is inferred but were not detected are shown in italics. 1, Trehalose synthesis from Glc phosphate and UDP-Glc; 2, trehalose breakdown by trehalase; 3, the PPP (also known as the hexose monophosphate pathway); 4, gluconeogenesis, starting with PEP and involving reversal of glycolysis with several differences; 5, glycolysis (the Embden-Meyerhoff-Parnas pathway); 6, non-photosynthetic one-carbon metabolism, typically involving tetrahydrofolate (THF) and S-adenosyl Met as carriers of the methyl groups; 7, lipolysis: storage lipid (tryacylglycerides) breakdown to glycerol and fatty acids, and subsequent glyoxysomal fatty acid β-oxidation to acetyl CoA; 8, Dark fixation of CO2 by pyruvate carboxylase to oxalocetate (8a) or carbamoyl P synthethase (8d); 9, glyoxylate cycle (or shunt) involving the production of glyoxylate from acetyl-CoA units via part of the TCA cycle; the glyoxylate is condensed with acetyl-CoA (from triacylglyceride degradation) to form triose and CO2; 10, TCA (also known as the Krebs cycle); 11, Arg synthesis by enzymes of the urea cycle including the incorporation of carbon from carbamoyl P.