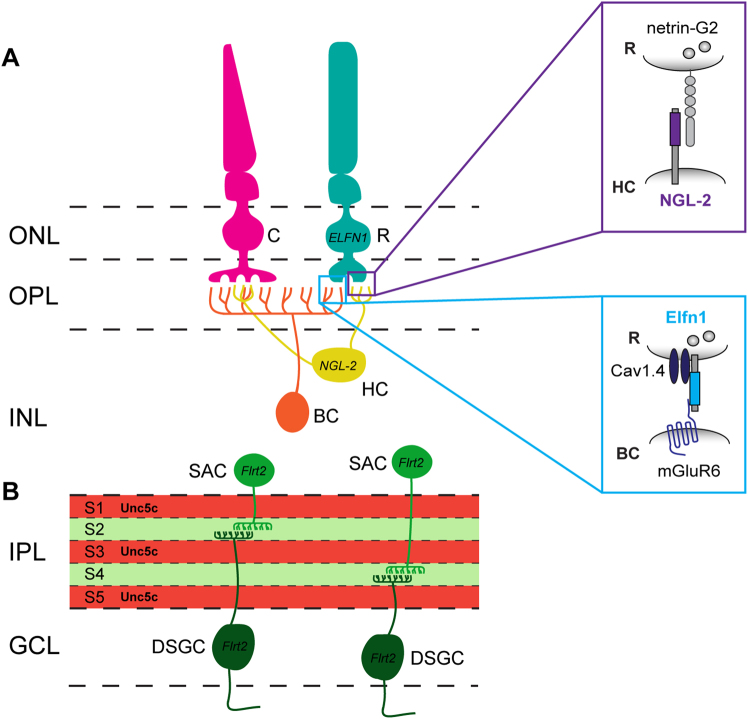
Fig. 3. LRR proteins mediate functional wiring of retinal synapses.
a Synaptic wiring in the outer plexiform layer. Photoreceptors (PR) form triad synapses with horizontal cells (HC) and bipolar cells (BC) in the outer plexiform layer (OPL). NGL-2 localizes to HC axon tips, which synapse onto netrin-G2-expressing rod PRs. NGL-2 KO causes HC axons to overshoot their laminar target, the OPL, and form fewer synapses with rod PRs, while HC dendrite—cone PR synapses that do not contain NGL-2 are unaffected. Elfn1 is expressed by rod PRs, which synapse onto ON-BCs in the OPL. Neighboring cone PR synapses formed on ON-BCs do not express Elfn1. Synaptic targeting of Elfn1 is mediated by α2δ4, an auxiliary subunit of the Cav1.4 channel. Once at the synapse, Elfn1 bridges a trans-synaptic complex between pre-synaptic, glutamate release-directing Cav1.4, and post-synaptic, glutamate-sensing mGluR6. Elfn1 KO in rod PRs disrupts the formation of rod PR synapses on ON-BCs, while neighboring cone PR synapses on ON-BCs are unaffected. b Laminar targeting in the inner plexiform layer. FLRT2 may mediate sublaminar targeting in the inner plexiform layer (IPL). FLRT2 protein is highly expressed in sublaminae (S) 2 and 4 of the IPL, where the dendrites of both starburst amacrine cells (SACs) and direction-selective ganglion cells (DSGCs) arborize. Unc5c is expressed in a complementary pattern in S1/3/5 of the IPL. FLRT2-expressing neurons are repelled by Unc5c in vitro, suggesting that Unc5c might restrict FLRT2-positive SAC and DSGC dendrites to S2/4 of the developing IPL. ONL outer nuclear layer, OPL outer plexiform layer, INL inner nuclear layer, IPL inner plexiform layer, GCL ganglion cell layer