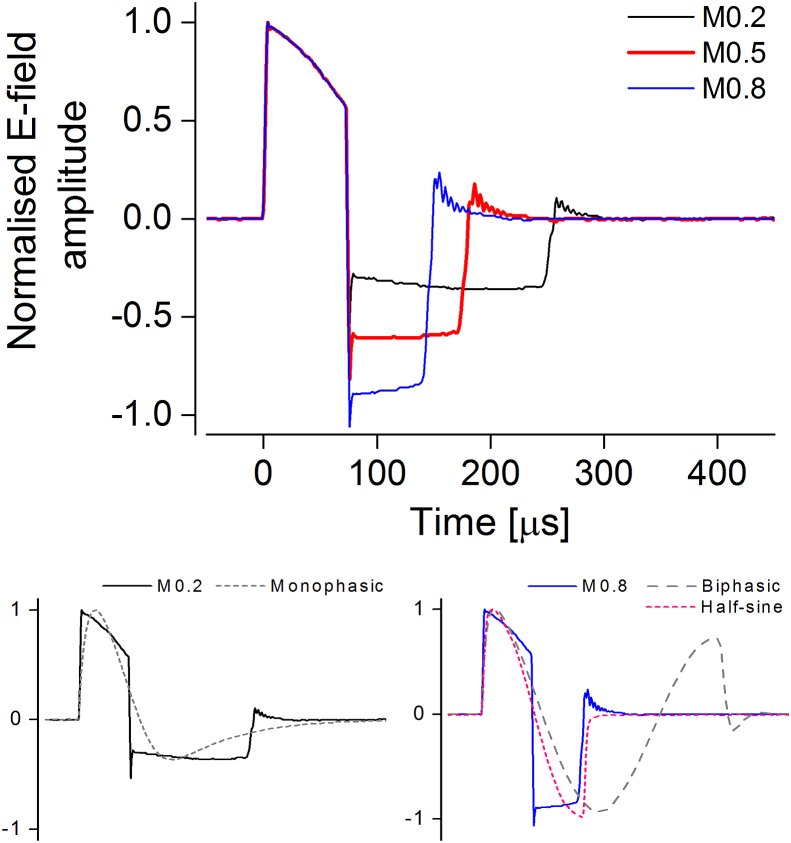
Fig. 1.
Types of TMS pulses used in this study. Current induced in a probe coil of 2 cm diameter held under the centre of a figure-of-eight-coil connected to a prototype cTMS device (Rogue Resolutions Ltd., Cardiff, United Kingdom), recorded and stored by an oscilloscope. So-called “positive monophasic” pulses with a pulse width of 75 μs and intensity of 20% of maximum stimulator output. Main figure illustrates cTMS pulses with distinct M-ratios: 0.2, 0.5 and 0.8, annotated in all figures as M0.2, M0.5 and M0.8, respectively. Amplitudes are normalised to the peak electric field recorded for each pulse. For comparison, conventional monophasic, half sine and biphasic pulse shapes are shown below. Note that the M0.8 pulse is more similar to a half sine than a biphasic pulse.