Fig. 2.
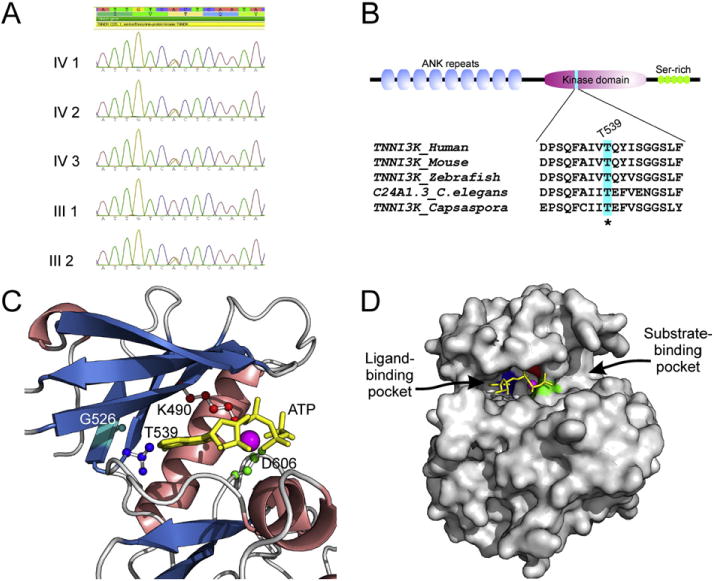
A) Sanger sequencing validation of TNNI3K (NM_015978.2:c.1615A>G; p.Thr539Ala) heterozygous variant identified by whole exome sequencing. B) Domain architecture of human TNNI3K and conservation of Thr539 position in animal lineage. C) Visualization of active site residues of human TNNI3K kinase domain together with ATP and Mg2+. Homology model was constructed using the Modeller9v11 program on the basis of four PDB templates, 3PPZ, 3KMW, 2EVA and 3BLQ, and evaluated by the ModFOLD program (score 0.81; any score >0.4 is a generally confident model). The α helices are shown in salmon, β sheets in blue, and loops in gray; catalytic residues Lys (K490) shown in red, Asp (D606) in green, Gly (G526) in light blue and gatekeeper residue Thr (T539) in dark blue; ATP in yellow and Mg2+ in purple. D) Surface view of ATP-binding pocket of human TNNI3K kinase domain in which the ATP and Mg2+ were hold by three key residues K490 in red, D606 in green and T539 in dark blue.
