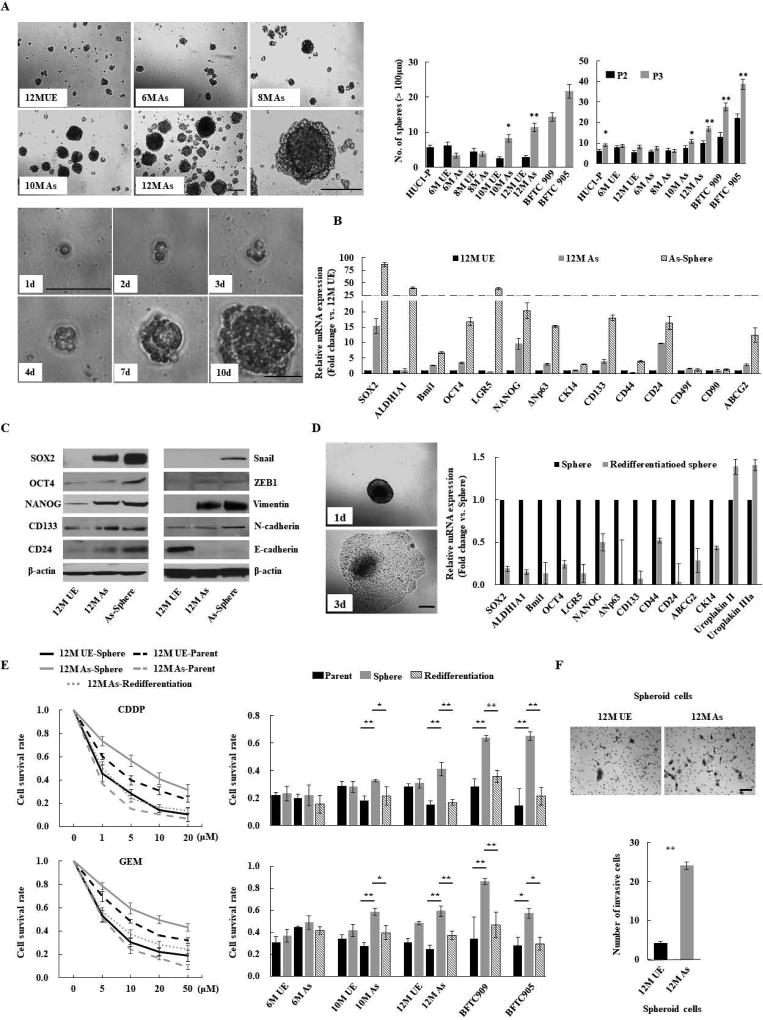
Figure 1.
Chronic arsenic exposure-induced malignant stemness properties in immortalized human urothelial cells (HUC1). (A) Sphere formation and self-renewal assays in chronic arsenic-exposed (As)-cells for 6 to 12 months (6M As- to 12M As-cells) compared with the passage-matched unexposed (UE)-cells. Upper left: representative images of spheres according to different time periods of arsenic exposure (scale bars, 200 µm); Lower left: representative consecutive images of secondary sphere formed from single spheroid 12M-As cell (scale bars, 200 µm). Right: the number of spheres over 100 µm; left bar graph: the number of spheres in As-cells and UE-cells; right bar graph: the number of spheroid cells after second (P2) and third (P3) passage in self-renewal assay. Data are from 3 independent experiments. BFTC 905 and 909 cell lines, established from arsenic exposed UCB subjects, were used as controls. (B) Relative expression of stemness-related molecules using Q-RT-PCR in parental or spheroid As-cells compared with UE-cells. (C) Western blotting of stem cell- and EMT-related molecules. (D) Spheroid As-cells-induced re-differentiation. When spheroid cells were cultured under standard conditions containing FBS, the floating spheroid cells could adhere and acquire epithelial morphology similar to parental cells (scale bars, 200 µm; left). The cells showed higher differentiation markers such as uroplakin II or IIIA, and lower stem cell markers compared with corresponding spheroid cells, as measured by Q-RT-PCR (right), indicating re-differentiation. (E) Chemo-resistance property of Spheroid As-cells. Left: cell viability determined by MTT assay after various concentrations of CDDP or GEM treatment for 72 hours in indicated cells. The ratio of absorbance values of various concentrations treatment related to the value of mock was considered as 1.0. Right: cell viability after 10 µM CDDP or GEM treatment of As-cells exposed at different time periods of arsenic. Spheroid cells were cultured in ultra-low attachment 96 well plates under serum-free condition. Spheroid As-cells were significantly more chemo-resistant than parental As- and re-differentiated cells. (F) Invasion assay of spheroid As-cells. Upper: representative images (scale bars, 100 µm); Lower: the number of invaded cells. Spheroid As-cells were a more invasive phenotype than spheroid UE-cells. Each error bar indicates mean ± SEM. * P <0.05, ** P <0.01 [Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test (A and F) and Kruskal-Wallis with post-hoc test (E)].