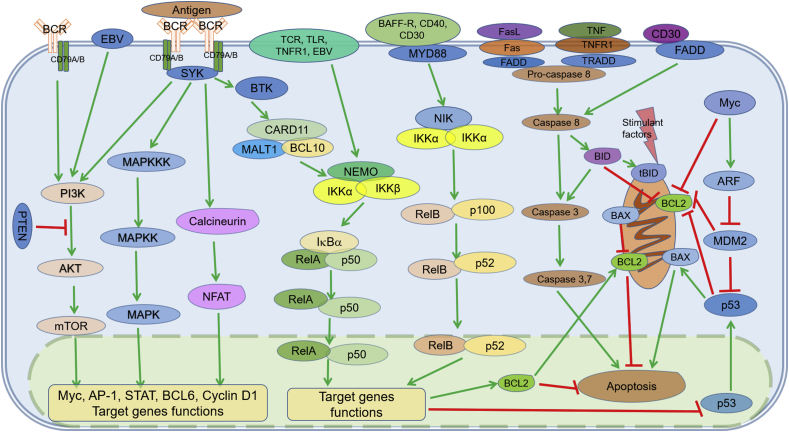
Fig. 1.
Illustration of cross-communication network of BCR, PI3K, apoptosis, and NF-κB signaling pathways. BCR, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, apoptosis, and NF-κB signaling pathways are independent but interconnected and may form complex crosstalk network. One pathway may act as upstream or downstream of other pathways and some molecular targets function as key points and players involved in several pathways. These key molecules have been shown promise to be a good therapeutic target for effective treatment in lymphoid malignancies. The green arrows indicate direction of activating signaling steps; the red bars indicate inhibitory signaling steps. AKT: v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog; ARF: alternative reading frame; AP-1: activator protein-1; BAFF-R: B-cell activating factor receptor; BAX: BCL2-associated X protein; BCL: B-cell leukemia/lymphoma; BCR: B-cell receptor; BID: BH3 interacting death agonist; BTK: Bruton's tyrosine kinase; CARD11: caspase recruitment domain family, member 11; CD: cluster of differentiation; EBV: Epstein–Barr virus; FADD: Fas associated via death domain; FasL: Fas ligand; IKK: IκB kinase; IκB: inhibitor of nuclear factor κB; MALT1: mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; MAPKK: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MAPKKK: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase; MDM2: mouse double minute-2 homolog; mTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin; MYD88: myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NEMO: NF-κB essential modifier; NFAT: nuclear factor of activated T-cells; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B; NIK: NF-κB-inducing kinase; PI3K: phosphoinositide-3-kinase; PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog; STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription; SYK: spleen associated tyrosine kinase; tBID: truncated BID; TCR: T-cell receptor; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; TNFR1: tumor necrosis factor receptor 1; TRADD: TNFRSF1A associated via death domain.