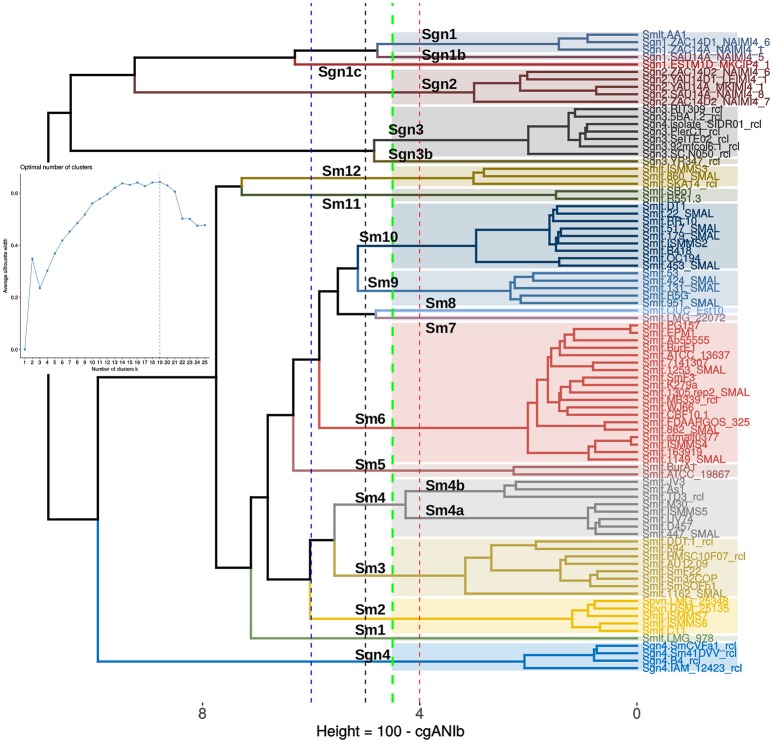
Figure 7.
Application of an unsupervised learning approach to the cgANIb distance matrix to identify statistically-consistent species-like clusters. The cgANIb matrix was converted to a distance matrix (cgANDb) and clustered using the Ward.D2 algorithm. The optimal number of clusters (k) was determined with the average silhouette-width statistic. The inset shows the statistic's profile, with k = 19 as the optimal number of clusters. This number corresponds to an cgANIb of 95.5% (gray dashed line). At a cgANDb of 4.1% (cgANIb = 95.9%) the groups delimited by the clustering approach are perfectly consistent with those delimited by the core- and pan-genome ML phylogenies displayed in Figures 5, 6, respectively.