Figure 1.
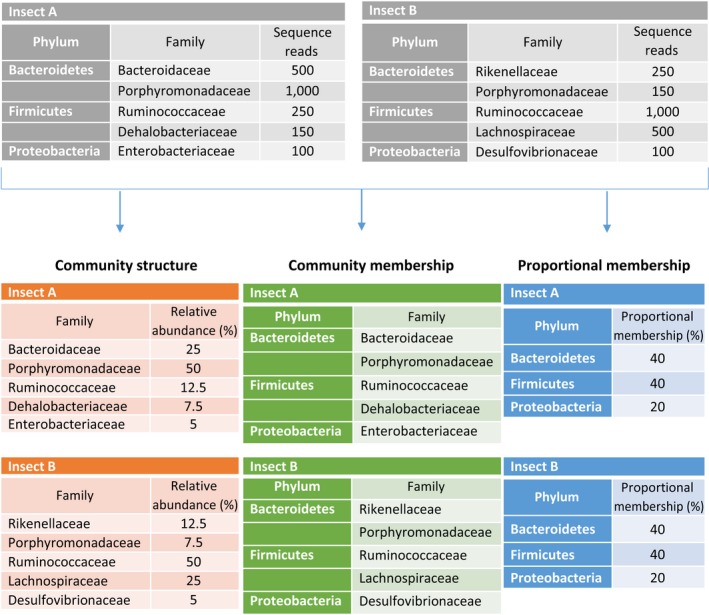
A hypothetical example of different community types in a sequencing data analysis. Sequencing results from the guts of two insects are analyzed based on the relative abundance of the sequence reads of individual taxon (Community structure), the presence or absence of microbial taxa in a sample (Community membership), and the fraction of the types of taxa that constitutes the community membership (Proportional membership). In this simplified example, Insect A and Insect B have different community structures and community memberships, as they have different abundances and different members, respectively, in the Family taxonomic level. However, both insects have identical proportional membership at Phylum level, with the same number of Family taxa under a Phylum taxon
