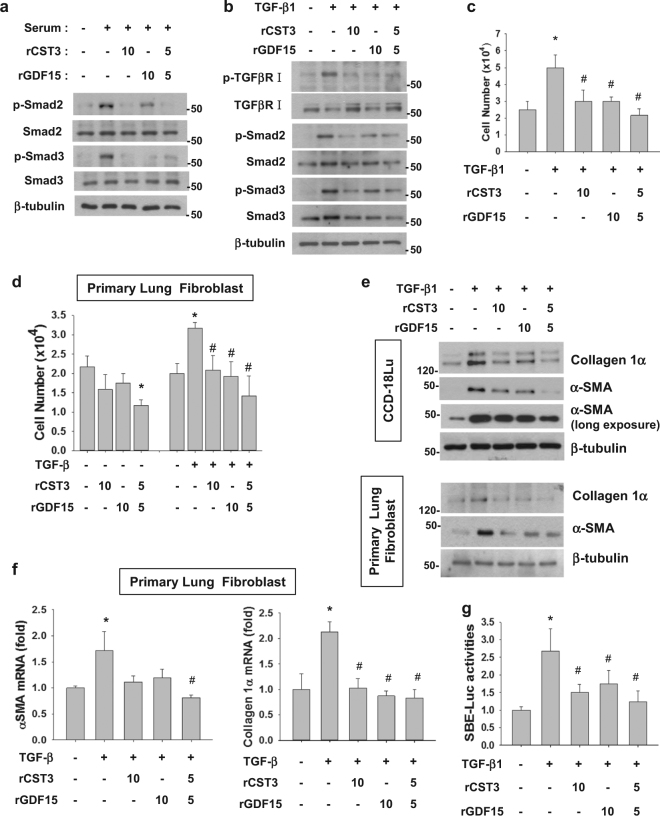
Fig. 5. CST3 and GDF15 inhibit the TGF-β signaling pathway in CCD-18Lu cells.
a,b CCD-18Lu cells, which had been pre-incubated in serum-free media for 16 h, were treated with a recombinant peptide (10 ng/mL) of CST3 or GDF15 in the presence of 5 % FBS (a) or 5 ng/mL TGF-β1 (b) for 1 h, and subjected to immunoblotting. c CCD-18Lu cells were pre-incubated in a serum-free medium for 16 h, and then treated with TGF-β1 and CST3 or/and GDF15 for 24 h. CCD-18Lu cells were counted using a hemocytometer. d Primary lung fibroblasts, which had been isolated from normal mouse lung, were pre-incubated in a serum-free medium for 16 h, and then treated with TGF-β1 and CST3 or/and GDF15 for 24 h. CCD-18Lu cells were counted using a hemocytometer. e CCD-18Lu cells or primary lung fibroblasts were treated with TGF-β1 and CST3 or/and GDF15 for 24 h, and subjected to immunoblotting. f Primary lung fibroblasts were treated with TGF-β1 and CST3 or/and GDF15 for 24 h. The mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR. g CCD-18Lu cells, which had been co-transfected with SBE-Luc and β-galactosidase plasmids, were treated with TGF-β1 and CST3 or/and GDF15 for 24 h. The luciferase activity was divided by β-galactosidase activity to normalize transfection efficiency. All data are presented as the means + s.d. from three experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. the untreated group; #P < 0.05 vs. the TGF-β1 only group by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test