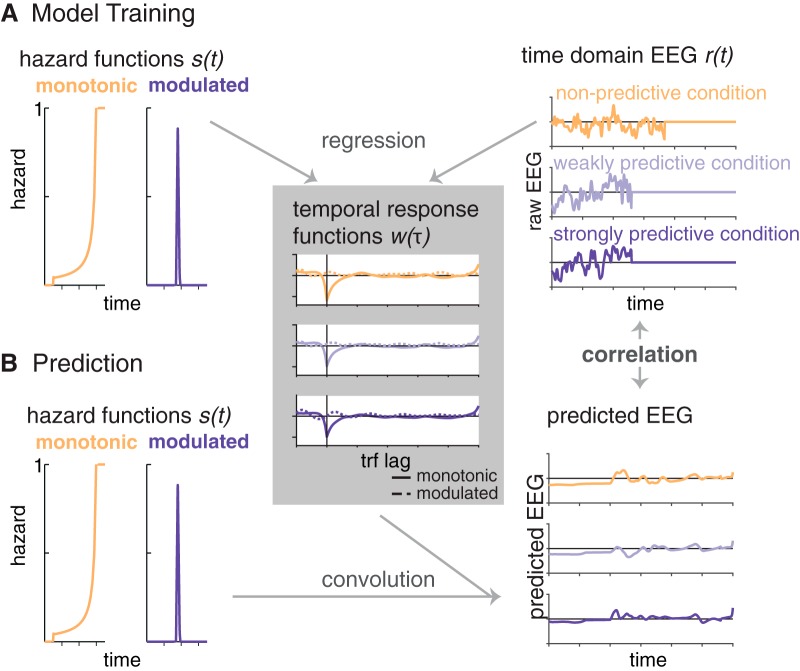
Figure 2.
Schematic depiction of the encoding model approach. A, One encoding model was computed per condition, by regressing the two hazard functions (s in Eq. 2) on the time-domain EEG data (r in Eq. 2; example trials are displayed, set to 0 at target onset. We obtained two temporal response functions (w in Eq. 2) per condition (right panel), one for the monotonic and one for the modulated hazard function. B, In a second step, we predicted EEG signals (example trials displayed in the bottom right panel) from each of the three models by convolving the hazard functions with the temporal response functions. Correlating the predicted and original EEG signals allowed us to test which model provides the best fit with the original EEG data.