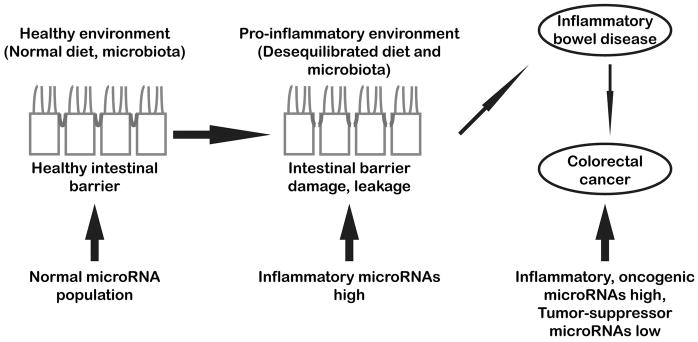
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram summarizing the main results and concepts discussed in this review. MicroRNAs are powerful regulators of cell homeostasis and function. Following IB damage, persistent inflammatory conditions can alter microRNA expression, initiating or accelerating the development of IBD. On the long run, chronic deregulation of microRNAs targeting transcripts encoding key components of IB as well as of oncogenic and tumor-suppressors microRNAs may lead to the development of colorectal cancer.