Figure 2.
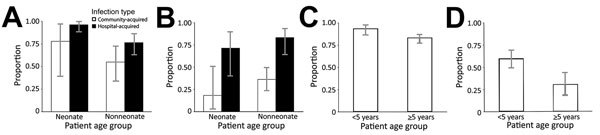
Antimicrobial resistance age trends, shown as proportion of resistant isolates from community-acquired and hospital-acquired infections, by patient age group, in children at Angkor Hospital for Children, Siem Reap, Cambodia, 2007–2016. A) Klebsiella pneumoniae third-generation cephalosporin resistance; B) Escherichia coli third-generation cephalosporin resistance; C) Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi multidrug resistance; D) Streptococcus pneumoniae penicillin resistance. Ages have been grouped into neonate (0–28 d) versus nonneonate (>29 d) or <5 years versus >5 y, as appropriate for the organism. Isolates were defined as hospital-acquired if taken >48 hours after admission. Error bars indicate 95% CIs.
