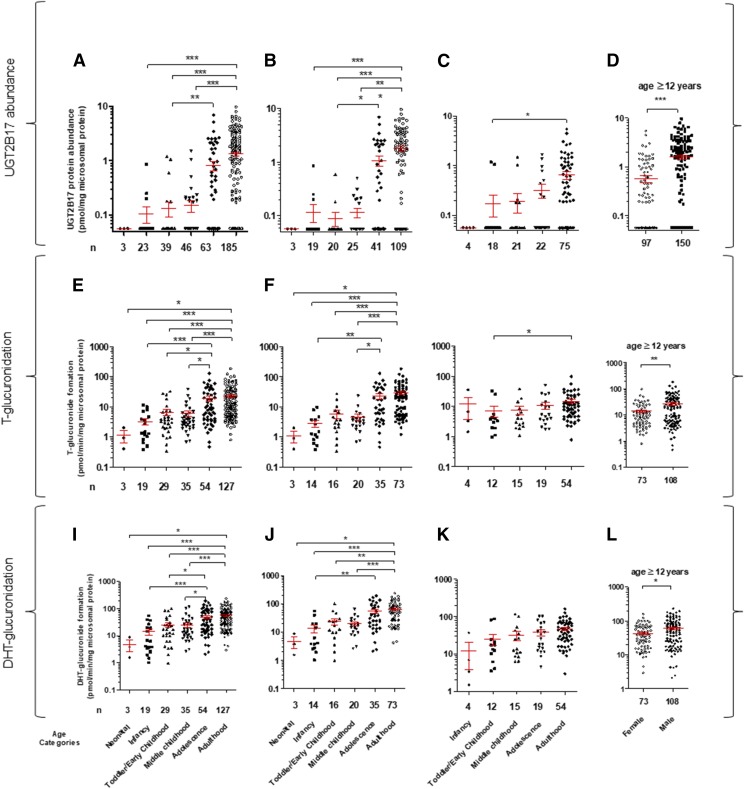
Fig. 2.
Categorical age-dependent UGT2B17 protein abundance (A–D), testosterone (T)-glucuronide formation (E–H), and DHT-glucuronide formation (I–L) data in all (A, E, and I), male (B, F and J) and female (C, G, and K) livers. The x-axis labels identifying data categories in the bottom panel (I–L) are also applicable to the corresponding top two panels (A–H). Number of samples is presented either as main label in the x-axis (A–H) or the x-axis parentheses (I–L). Donors with zero UGT2B17 gene copy were excluded from this analysis. Of 375 samples (male plus female), 205 were lower than the LOD of UGT2B17 protein measurement. For statistical analysis, samples <LOD (excluding zero copy number) were assigned a value of 0.06 pmol/mg of microsomal protein, which was one-third the LLOQ (0.17 pmol/mg of microsomal protein). UGT2B17 was sparsely (12 of 92 samples) detected in children younger than the age of 9 years. An association of age with UGT2B17 abundance or testosterone and DHT-glucuronide formation was more prominent in male versus. female. Mean UGT2B17 protein abundance and testosterone- and DHT-glucuronide formation in these samples was 2.8-, 1.9-, and 1.4-fold greater in male versus female donors aged ≥12 years, respectively (D). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.0001.