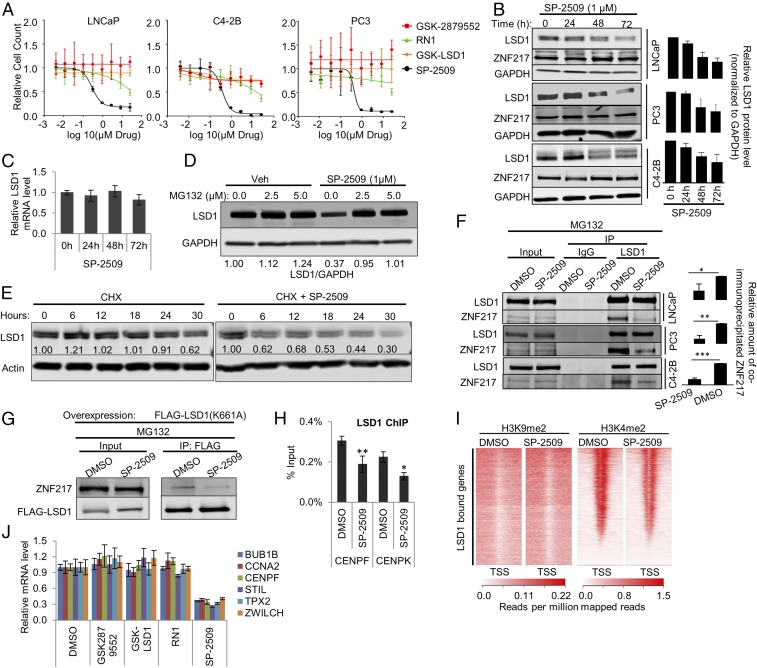
Fig. 5.
Treatment with SP-2509, a reversible LSD1 inhibitor, recapitulates the effect of LSD1 RNAi. (A) Cell growth rate of LNCaP, C4-2B, and PC3 cells treated with dose escalation of the LSD1 inhibitors GSK-LSD1, GSK2879552, RN-1, and SP-2509. The relative number of viable cells was measured by staining live cells in situ with Hoechst 33342 and NucGreen Dead dyes (Life Technologies) and capturing one 4× fluorescent field per well using a BioTek Cytation 5 imager (BioTek Instruments, Inc.) Cell-growth curves were fitted by nonlinear regression. See also Fig. S7A. (B, Left) Immunoblot showing a time-dependent effect of SP-2509 on LSD1 and ZNF217 protein levels in LNCaP, C4-2B, and PC3 cell lines. The cells were treated with 1 µM SP-2509. The lysates were prepared at the indicated time points after treatment and were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (Right) The relative intensity of LSD1 bands normalized to the intensity of GAPDH bands in each sample (n = 3). Data are reported as ±SD. (C) qRT-PCR results showing the relative LSD1 mRNA levels after 24, 48, or 72 h treatment with 1 µM SP-2509. The data were normalized to actin mRNA levels. Data are reported as ±SD. (D) Immunoblot showing the effect of MG-132 treatment on SP-2509–induced LSD1 protein depletion. The cells were treated with either DMSO or 1 µM SP-2509. Twenty-four hours later, cells were treated with vehicle or the indicated dose of MG132. Cell lysates were prepared 16 h after MG132 treatment and were immunoblotted using the indicated antibodies. (E) Immunoblot showing the effect of SP-2509 on the half-life of LSD1 protein. LNCaP cells were treated with 10 µg/mL cycloheximide (CHX) alone or in combination with 1 µM SP-2509. The cell lysates were prepared at 0, 6, 12, 18, 24, and 30 h after the treatment and were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (F, Left) SP-2509 disrupts the interaction of LSD1 with ZNF217. The cells were treated with DMSO vehicle or 1 µM SP-2509 for 24 h. Then 2.5 µM MG132 was added to the medium. Lysates were prepared 16 h later for IP analyses using immobilized anti-LSD1 antibody. The eluates were immunoblotted for LSD1 and ZNF217. (Right) The relative intensity of the coimmunoprecipitated ZNF217 band normalized to the intensity of immunoprecipitated FLAG-LSD1 band. Three independent immunoprecipitations/immunoblots were performed. (G) SP-2509 disrupts the interaction of catalytically deficient K661A LSD1 with ZNF217. LNCaP cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged catalytically deficient K661A LSD1 plasmid. Twenty-four hours after the transfection, the cells were treated with either DMSO vehicle or 1 µM SP-2509. Twenty-four hours later 2.5 µM MG132 was added to the medium. Cells lysates were prepared 48 h after SP-2509 treatment. FLAG-tagged LSD1 (K661A) was immunoprecipitated using immobilized antibody against FLAG, and the eluates were analyzed by immunoblots using antibodies against ZNF217 and FLAG. (H) SP-2509 depletes LSD1 from target gene promoters. LNCaP cells were treated with DMSO vehicle or 1 µM SP-2509. LSD1 ChIP-PCR was performed 24 h after the treatment. Enrichment was calculated as percentage of input (n = 4). The data are reported as ±SD. (I) H3K4me2 and H3K9me2 ChIP-seq peaks after SP-2509 are shown around the TSS of the genes previously shown to be bound by LSD1 (21). (J) qRT-PCR results for LSD1-regulated target genes after 72 h of treatment with the LSD1 inhibitors GSK-LSD1, GSK2879552, RN-1, and SP-2509. In B, C, F, H, and J, the data are reported as ±SD; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, two-tailed unpaired t test.