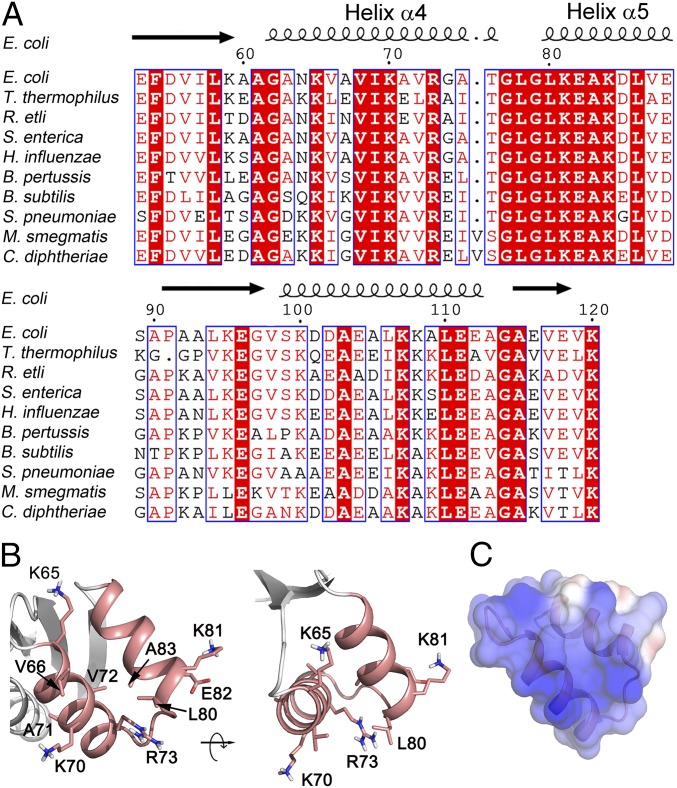
Fig. 1.
Sequence and structure analysis of E. coli L12-CTD with focus on helices 4/5. (A) Sequence alignment of L12-CTD from the bacteria E. coli, Thermus thermophilus, Rhizobium etli, Salmonella enterica, Haemophilus influenzae, Bordetella pertussis, Bacillus subtilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Mycobacterium smegmatis, and Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Strictly conserved amino acids are highlighted in red. Moderately conserved residues are in red letters. The secondary structure of L12-CTD is indicated above the alignment. (B) Ribbon illustration of the helices 4/5 (salmon) from the crystal structure of L12-CTD (4) (PDB 1CTF) showing the side chains of the conserved residues suggested to be involved in tr-GTPase interactions (5). (C) Electrostatic surface potential representation of the helices 4/5 on the L12-CTD. Blue and red in C correspond to positive and negative potentials, respectively.