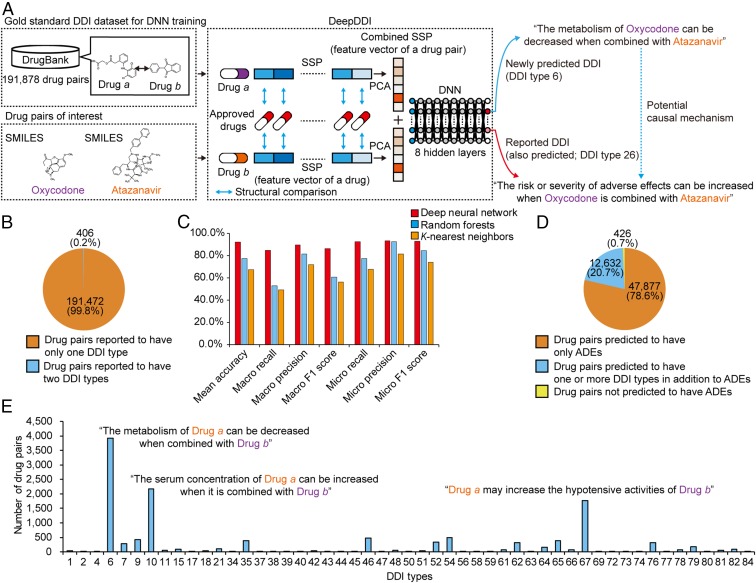
Fig. 1.
Overall scheme, performance evaluation, and application of DeepDDI. (A) DeepDDI consists of the structural similarity profile (SSP) generation pipeline and deep neural network (DNN). DeepDDI accepts chemical structures (in SMILES describing the structure of a chemical compound) and names of drugs in pairs as inputs, and predicts their potential drug–drug interaction (DDI) types as outputs in human-readable sentences having the input drug names. DNN of DeepDDI is a multilabel classification model that can predict multiple DDI types at the same time for a given drug pair. To develop DeepDDI, a gold standard DDI dataset covering 191,878 drug pairs was obtained from DrugBank, and used to train the DNN of DeepDDI. A single, combined SSP (feature vector of a drug pair) is generated for each input drug pair (SI Appendix, Materials and Methods). DeepDDI has many implications such as prediction of potential causal mechanism for the adverse drug evens (ADEs) of a drug pair of interest (blue dotted arrow) using the output sentences. It should be noted that the use of input data on the same drug pairs, but with different drug orders, results in different DeepDDI output sentences. For example, the use of input data in the order of atazanavir and oxycodone generated a DeepDDI output sentence corresponding to the DDI type 26 with atazanavir appearing before oxycodone; and the output sentence for DDI type 6 was not generated in this case. (B) Number (percentage) of drug pairs in the gold standard DDI dataset having a single DDI type or two. The dataset does not have drug pairs having more than two DDI types. (C) Prediction performance of DeepDDI for classifying DDI types for drug pairs in the gold standard DDI dataset using three different machine learning algorithms (SI Appendix, Materials and Methods). (D) DeepDDI prediction results for the drug pairs reported to have ADEs in the gold standard DDI dataset. (E) Number of drug pairs having additionally predicted DDI types using DeepDDI in addition to the reported ADEs.