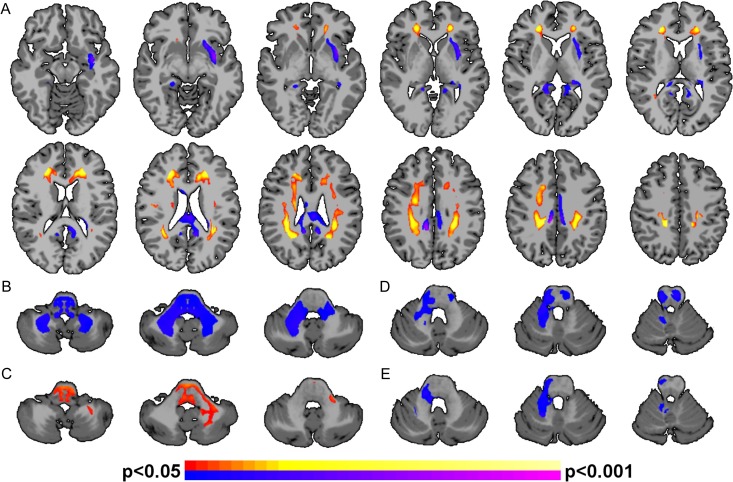
Figure 2.
Alterations in white matter for PT participants. (A) PT participants exhibited significantly (P < 0.05, corrected) altered FA in several white matter tracts. Regions of significantly greater FA for the PT participants compared with terms include bilateral posterior, mid-, and anterior corona radiata and forceps minor (shown in hot colors); regions of significantly reduced FA for the PT participants compared with terms include the left external capsule, corpus body, and corpus splenium (shown in cool colors). (B) GPT scores, (C) VMI, (D) ROCF Copy, and (E) ROCF Immediate scores were significantly correlated (P < 0.05, corrected) with FA in the cerebellum white matter for PT participants. Higher FA were associated with lower (improved) GPT scores, higher (improved) VMI scores, lower (worse) ROCF Copy, and lower (worse) ROCF Immediate scores. Positive correlations between neurocognitive testing and FA are shown in hot colors; negative correlations between neurocognitive testing and FA are shown in cool colors. No correlations in the cerebellum were observed for the term participants.