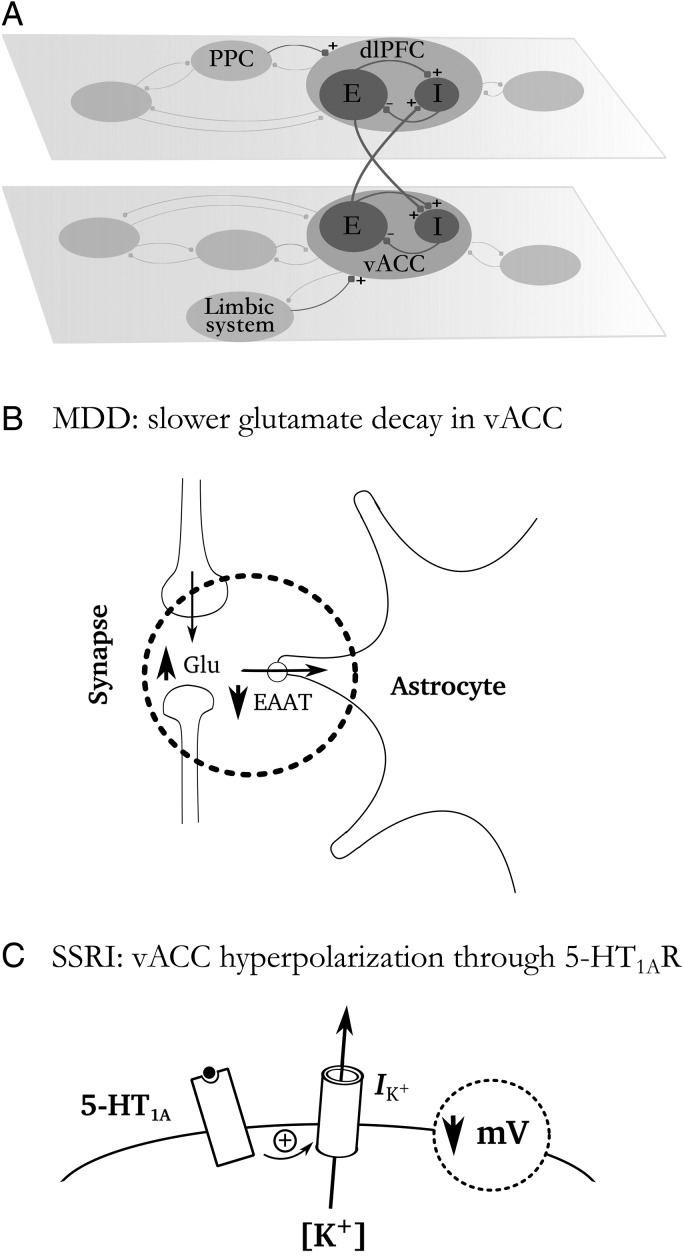
Figure 1.
Schematic of network architecture and mechanisms. (A) The conceptual network model included 2 subsets of networks: (1) The emotional network including vACC and (2) the cognitive network including dlPFC. The vACC and dlPFC are the hubs of each network, reciprocally connected via disynaptic inhibition. Each subnetwork included recurrently coupled excitatory pyramidal cells (E cells) and inhibitory interneurons (I cells). Emotional inputs from the limbic system target vACC and cognitive inputs from posterior parietal cortex (PPC) impinge on dlPFC. (B) Schematic drawing illustrating the slower glutamate reuptake in vACC described in MDD, which we simulated as a slow-down of glutamate decay in the synapses. (C) Schematic drawing illustrating the action of SSRIs through 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT1A) receptors: An increase in an outward K+ current causes a small hyperpolarization of vACC excitatory cells, which is what we simulate computationally.