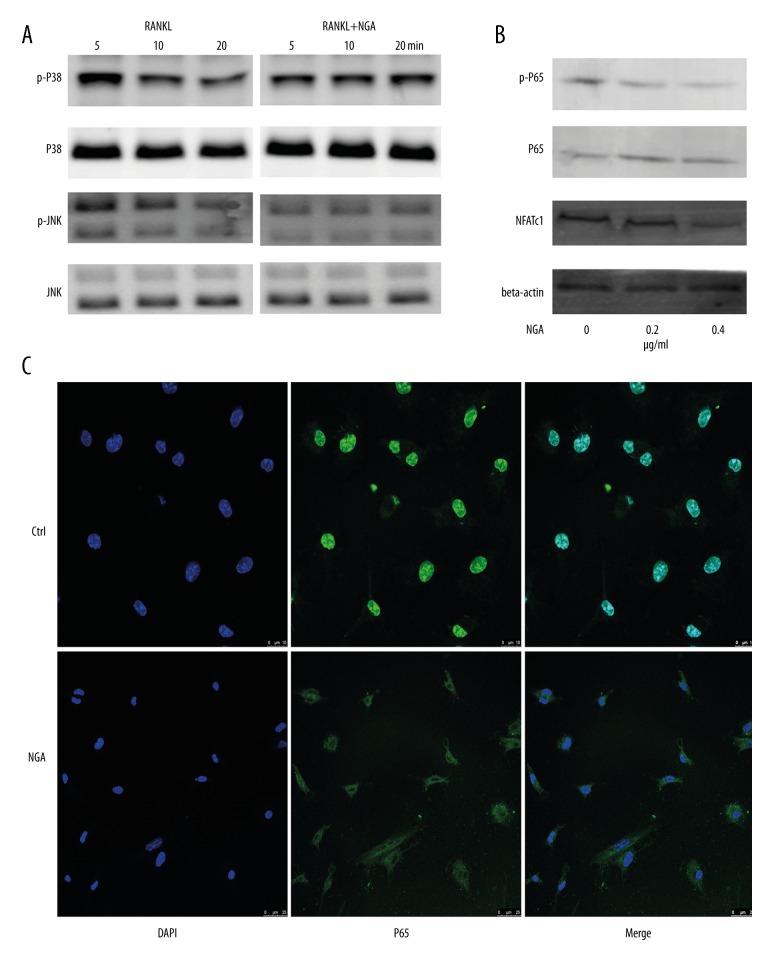
Figure 4.
NGA inhibited the JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways in mouse BMMs in vitro. (A) Mouse BMMs were pretreated with 0.4 μg/ml NGA for 2 hours. The cells were then stimulated with 50 ng/ml of RANKL for 5, 10, or 20 minutes to detect the expression of key proteins in multiple BMM signaling pathways and their corresponding phosphorylation levels. (B) The effect of NGA on the p65 signaling pathway and NFATc1 expression. To determine p65 signaling pathway, BMMs were pretreated with 0, 0.2 or 0.4 μg/ml NGA for 2 hours and then stimulated with 50 ng/ml RANKL for 30 minutes. To determine the effect of NGA son NFATc1, BMMs were treated with 50 ng/ml RANKL, and increasing concentrations of NGA (0, 0.2, 0.4 μg/ml) for three days. (C) Confocal fluorescence microscopy shows the effects of NGA on p65 nuclear translocation in BMMs cultured with 30 ng/ml M-CSF in 0 or 0.4 μg/ml NGA for 2 hours and then treated with 50 ng/ml of RANKL for 30 minutes are shown. All cells were fixed and stained with the red-orange fluorophore, rhodamine phalloidin.