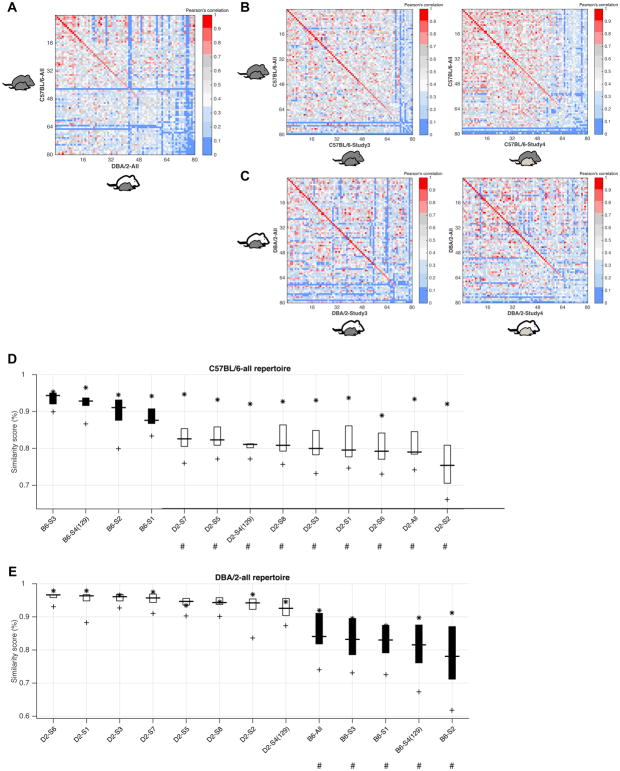
Figure 7. Syllable repertoire stability in the parental strains across replicate studies.
(A) Similarity Matrix used to assess the similarity of the spectral shape of pairs of repertoire units (RUs) learned from the full C57BL/6 and DBA/2 datasets (“C57BL/6-All”, “DBA/2-All”) when these strains were paired with a C57BL/6 juvenile partner (X-axis, DBA/2 (white) with juvenile C57BL/6 (black) mouse; Y-axis, C57BL/6 (black) with juvenile (black) C57BL/6 mouse.
(B) Similarity Matrices computed between the full C57BL/6 repertoire (Y-axis) and individual studies in which the C57BL/6 strain was tested with a C57BL/6 (left panel) or 129S1 (right panel; light gray) juvenile, showing high repertoire similarity regardless of partner strain.
(C) Similarity Matrices computed between the full DBA/2 repertoire (Y-axis) and individual studies in which the DBA/2 strain was tested with a C57BL/6 (left panel) or 129S1 (right panel) juvenile, showing high repertoire similarity regardless of partner strain.
(D–E) Similarity Boxplot representation of RU similarity. Repertoires built from 4 distinct studies with C57BL/6 (B6) mice and 8 distinct studies with DBA/2 (D2) mice (individual studies are listed on the X-axis) in comparison with full repertoires built from all C57BL/6 and DBA/2 studies conducted with C57BL/6 juveniles. The B6 and D2 studies conducted with 129S1 juvenile partners (Study 4, S4) are also shown. # Indicates ‘comparison’ strains (X-axis) with statistically significant differences in average repertoire similarity compared to the ‘reference’ repertoire (title). P < 0.05.