Fig. 3. Silencing-prone transgenes can be expressed in the germline by avoiding piRNA targeting.
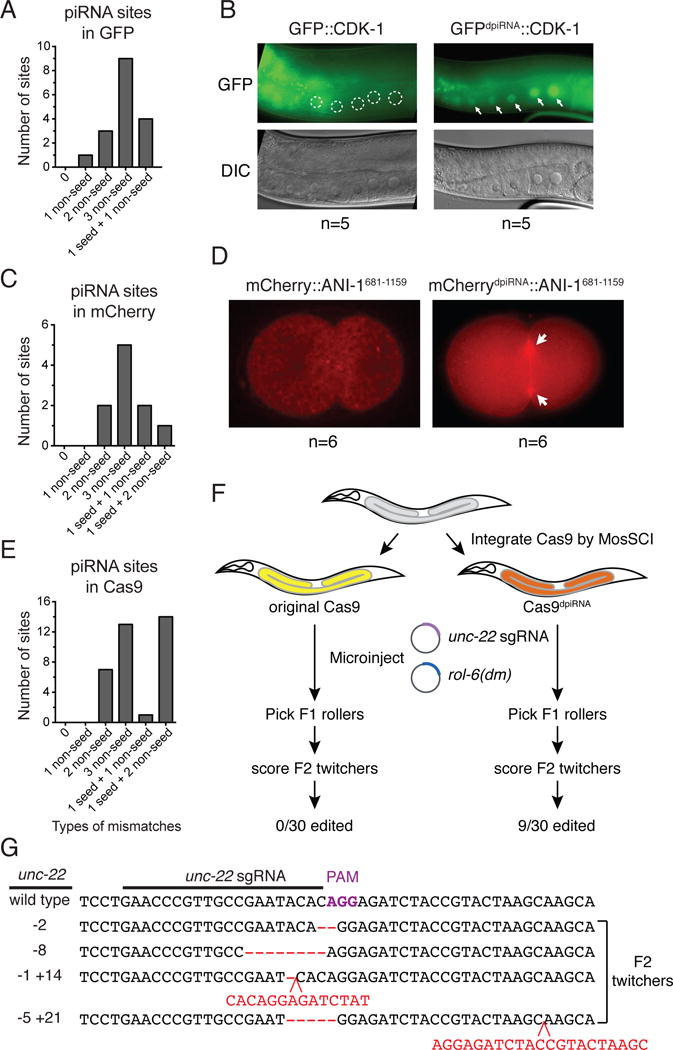
(A) Predicted piRNA sites in GFP mRNA sequence. The numbers of piRNA sites that contain different types of mismatches are shown. The relaxed criteria are used to predict piRNA sites on transgenes: all GU wobble pairing is allowed (considered as paired), and up to 3 non-GU mismatches are allowed when sites have perfect seed pairing, or up to 1 non-GU mismatches are allowed when sites have 1 non-GU mismatches in the seed region. The mismatch at the first nucleotide of a piRNA is not counted/considered.
(B) The expression of original GFP∷CDK-1 that contains the predicted piRNA targeting sites, or the modified GFPdpiRNA∷CDK-1where all predicted piRNA sites have been removed by introducing silent mutations (right). Arrows mark the germline nuclei with expressed GFPdpiRNA∷CDK-1. Circles mark the germline nuclei with silenced GFP∷CDK-1.
(C) Predicted piRNA sites in mCherry mRNA sequence (left).
(D) The expression of original mCherry∷ANI-1681-1159 that contains the predicted piRNA targeting sites, or the modified mCherrydpiRNA∷ANI-1681-1159 where the predicted piRNA sites have been removed by introducing silent mutations (right). Arrows mark the expression of mCherrydpiRNA∷ANI-11681-1159 at cleavage furrows of the one-cell embryo.
(E) Predicted piRNA sites in Cas9 mRNA sequence.
(F) A schematic showing the procedure followed to examine if genome editing occurs in transgenic animals that carry the original or modified Cas9 transgenes. Plasmids containing unc-22 sgRNA and rol-6(su1006) dominant transformation marker plasmid are co-injected into transgenic animals that have been carrying the Cas9 transgene for over 5 generations. F1 transformed roller animals are picked and their F2 progeny are scored for unc-22 gene editing through twitcher phenotype.
(G) Sequences of various unc-22 edited alleles obtained in the animals carrying the modified Cas9 transgene injected with plasmid encoding unc-22 sgRNA. Indels are highlighted in red.
