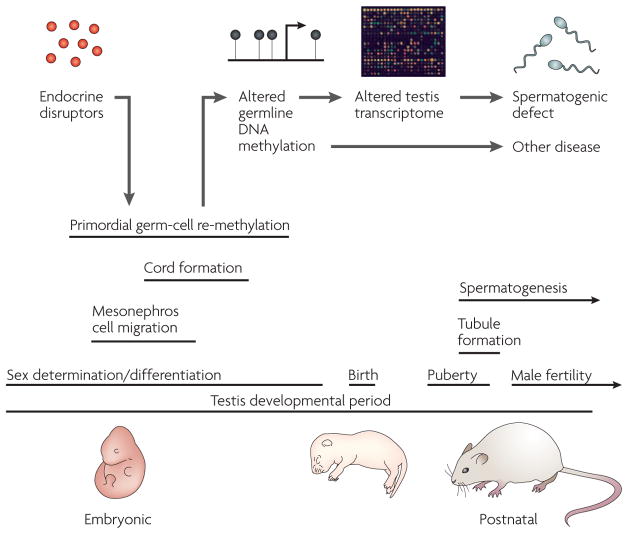
Figure 6. A model for endocrine-disruptor-induced epigenetic transgenerational disease.
Endocrine-disruptor action reprogrammes the epigenome of the developing germ cell during embryonic sex determination, leading to genes and other DNA sequences with altered DNA methylation97. These changes are proposed to alter the transcriptomes of the testis and other organs, thereby promoting adult pathologies, some of which are inherited transgenerationally. Epigenetic mechanisms might therefore have a role in the induction of adult-onset disease through environmental exposures early in development.