Figure 3.
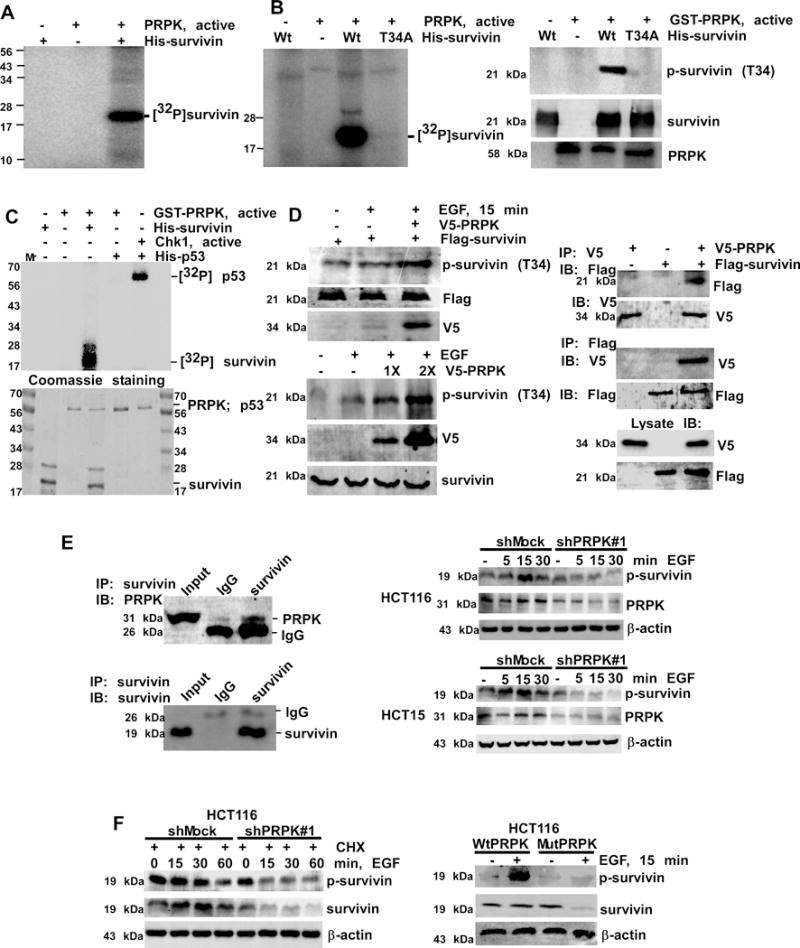
PRPK phosphorylates survivin and increases its stability. A, survivin is phosphorylated by PRPK in vitro. B, wild-type survivin (Wt) or a survivin Thr34Ala mutant (T34A) was used as a substrate for PRPK. Reactive products were visualized by autoradiography (left panel) or Western blotting (right panels). C, phosphorylation of survivin or p53 by PRPK in an in vitro kinase assay (upper panel). Phosphorylation of p53 by Chk1 is a positive control. Coomassie blue staining was used to verify equal loading of proteins (lower panel). D, left, PRPK phosphorylates survivin in cells treated with EGF. Equal amounts of pcDNA3-V5-PRPK and pcDNA-Flag-survivin (upper panels) or increasing amounts of pcDNA3-V5-PRPK (lower panels) were transiently transfected into HEK293 cells and phosphorylation of survivin was detected by Western blotting. D, right, PRPK binds with survivin in HEK293 cells. PcDNA3-V5-PRPK and pcDNA3-Flag-survivin were co-transfected into cells, immuno-precipitated with anti-V5 (upper panels) or anti-Flag (middle panels) to precipitate PRPK or survivin and probed with anti-Flag or anti-V5, respectively. Cell lysates were used to verify transfection efficiency of V5-PRPK and Flag-survivin (bottom panels). E, left, survivin binds with PRPK in HCT116 cells. Endogenous survivin was immunoprecipitated and probed with anti-PRPK. E, right, phosphorylation of survivin is decreased in shPRPK/ HCT116 (upper panels) or shPRPK/HCT15 (bottom panels) cells. The total levels of PRPK confirmed PRPK deficiency. F, cells were treated with CHX followed by EGF and then survivin stability was detected (left panels). The p-survivin or total survivin proteins were decreased in EGF-treated mutant (Mut) PRPK cells (right panels). β-Actin levels were used as loading controls.
